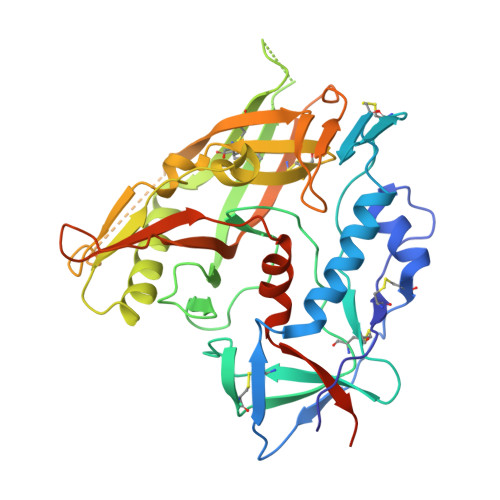
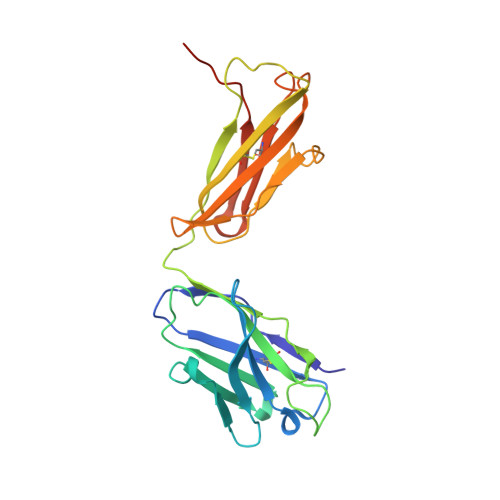
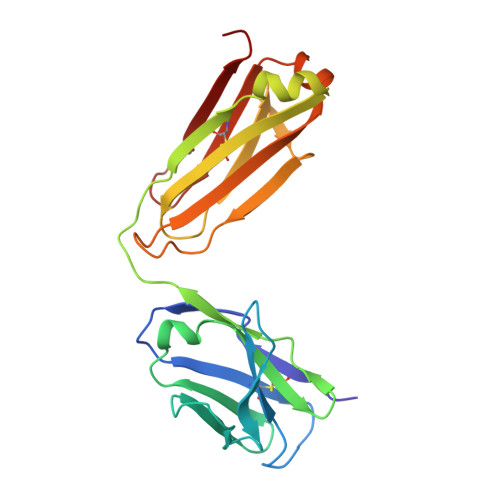
Vaccination induces maturation in a mouse model of diverse unmutated VRC01-class precursors to HIV-neutralizing antibodies with >50% breadth.
Chen, X., Zhou, T., Schmidt, S.D., Duan, H., Cheng, C., Chuang, G.Y., Gu, Y., Louder, M.K., Lin, B.C., Shen, C.H., Sheng, Z., Zheng, M.X., Doria-Rose, N.A., Joyce, M.G., Shapiro, L., Tian, M., Alt, F.W., Kwong, P.D., Mascola, J.R.(2021) Immunity 54: 324-339.e8
- PubMed: 33453152
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2020.12.014
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7JKS, 7JKT - PubMed Abstract:
Vaccine elicitation of broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) is a key HIV-research goal. The VRC01 class of bnAbs targets the CD4-binding site on the HIV-envelope trimer and requires extensive somatic hypermutation (SHM) to neutralize effectively. Despite substantial progress, vaccine-induced VRC01-class antibodies starting from unmutated precursors have exhibited limited neutralization breadth, particularly against viruses bearing glycan on loop D residue N276 (glycan276), present on most circulating strains. Here, using sequential immunization of immunoglobulin (Ig)-humanized mice expressing diverse unmutated VRC01-class antibody precursors, we elicited serum responses capable of neutralizing viruses bearing glycan276 and isolated multiple lineages of VRC01-class bnAbs, including two with >50% breadth on a 208-strain panel. Crystal structures of representative bnAbs revealed the same mode of recognition as known VRC01-class bnAbs. Structure-function studies further pinpointed key mutations and correlated their induction with specific immunizations. VRC01-class bnAbs can thus be matured by sequential immunization from unmutated ancestors to >50% breadth, and we delineate immunogens and regimens inducing key SHM.
Organizational Affiliation:
Vaccine Research Center, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA.