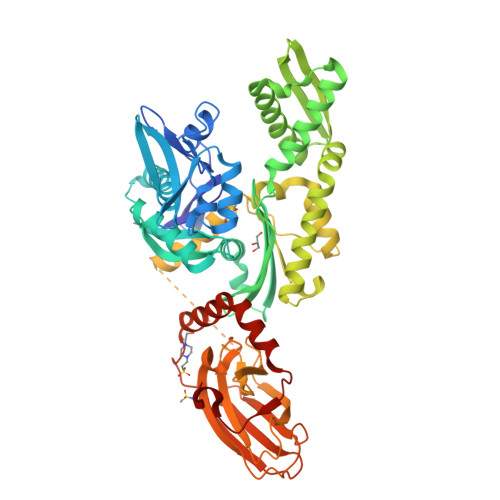
Combined In-Solution Fragment Screening and Crystallographic Binding-Mode Analysis with a Two-Domain Hsp70 Construct.
Zehe, M., Kehrein, J., Schollmayer, C., Plank, C., Kovacs, H., Merino Asumendi, E., Holzgrabe, U., Grimm, C., Sotriffer, C.(2024) ACS Chem Biol
- PubMed: 38317495
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.3c00589
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6H54, 7O6R, 7ODB, 7ODD, 7ODI, 7PLK - PubMed Abstract:
Heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) isoforms are key players in the regulation of protein homeostasis and cell death pathways and are therefore attractive targets in cancer research. Developing nucleotide-competitive inhibitors or allosteric modulators, however, has turned out to be very challenging for this protein family, and no Hsp70-directed therapeutics have so far become available. As the field could profit from alternative starting points for inhibitor development, we present the results of a fragment-based screening approach on a two-domain Hsp70 construct using in-solution NMR methods, together with X-ray-crystallographic investigations and mixed-solvent molecular dynamics simulations. The screening protocol resulted in hits on both domains. In particular, fragment binding in a deeply buried pocket at the substrate-binding domain could be detected. The corresponding site is known to be important for communication between the nucleotide-binding and substrate-binding domains of Hsp70 proteins. The main fragment identified at this position also offers an interesting starting point for the development of a dual Hsp70/Hsp90 inhibitor.
Organizational Affiliation:
University of Würzburg, Institute of Pharmacy and Food Chemistry, Am Hubland, DE-97074 Würzburg, Germany.