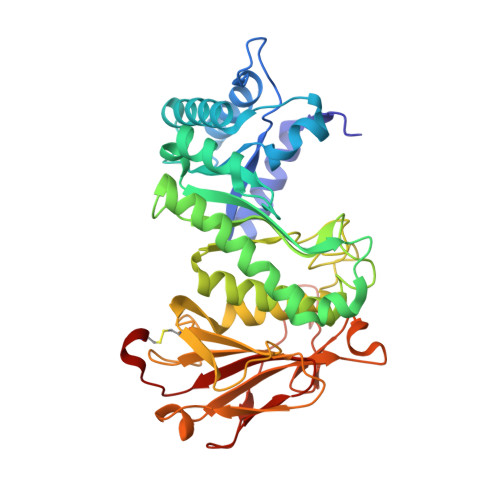
Computational design and experimental characterisation of a stable human heparanase variant.
Whitefield, C., Hong, N., Mitchell, J.A., Jackson, C.J.(2022) RSC Chem Biol 3: 341-349
- PubMed: 35382258
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d1cb00239b
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7RG8 - PubMed Abstract:
Heparanase is the only human enzyme known to hydrolyse heparin sulfate and is involved in many important physiological processes. However, it is also unregulated in many disease states, such as cancer, diabetes and Covid-19. It is thus an important drug target, yet the heterologous production of heparanase is challenging and only possible in mammalian or insect expression systems, which limits the ability of many laboratories to study it. Here we describe the computational redesign of heparanase to allow high yield expression in Escherchia coli . This mutated form of heparanase exhibits essentially identical kinetics, inhibition, structure and protein dynamics to the wild type protein, despite the presence of 26 mutations. This variant will facilitate wider study of this important enzyme and contributes to a growing body of literature that shows evolutionarily conserved and functionally neutral mutations can have significant effects on protein folding and expression.
Organizational Affiliation:
Research School of Chemistry, Australian National University Canberra ACT, 2601 Australia colin.jackson@anu.edu.au.