Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 neutralization by shark variable new antigen receptors elucidated through X-ray crystallography.
Ubah, O.C., Lake, E.W., Gunaratne, G.S., Gallant, J.P., Fernie, M., Robertson, A.J., Marchant, J.S., Bold, T.D., Langlois, R.A., Matchett, W.E., Thiede, J.M., Shi, K., Yin, L., Moeller, N.H., Banerjee, S., Ferguson, L., Kovaleva, M., Porter, A.J., Aihara, H., LeBeau, A.M., Barelle, C.J.(2021) Nat Commun 12: 7325-7325
- PubMed: 34916516
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27611-y
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7SPO, 7SPP - PubMed Abstract:
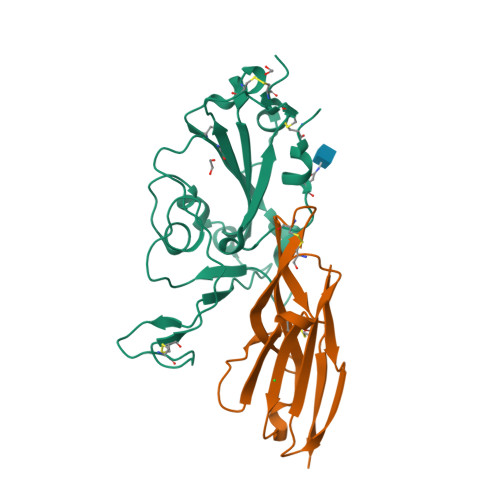
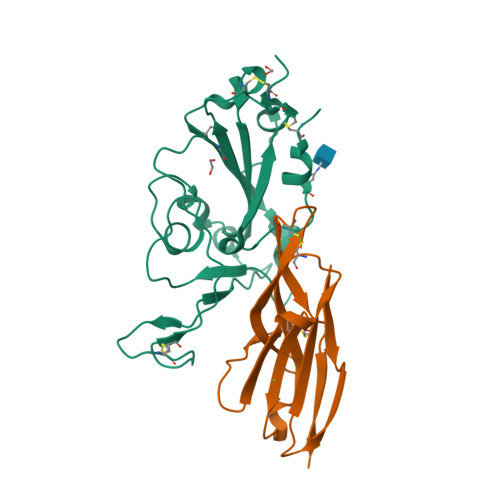
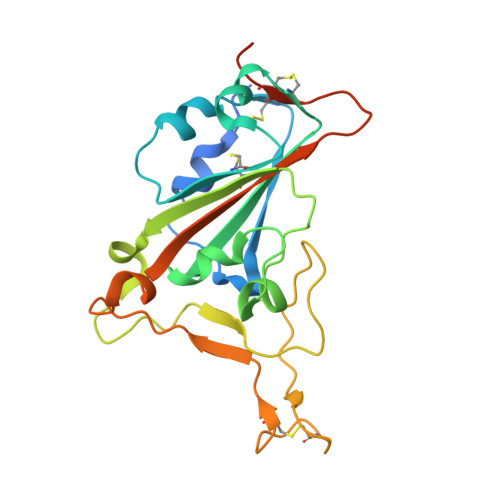
Single-domain Variable New Antigen Receptors (VNARs) from the immune system of sharks are the smallest naturally occurring binding domains found in nature. Possessing flexible paratopes that can recognize protein motifs inaccessible to classical antibodies, VNARs have yet to be exploited for the development of SARS-CoV-2 therapeutics. Here, we detail the identification of a series of VNARs from a VNAR phage display library screened against the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain (RBD). The ability of the VNARs to neutralize pseudotype and authentic live SARS-CoV-2 virus rivalled or exceeded that of full-length immunoglobulins and other single-domain antibodies. Crystallographic analysis of two VNARs found that they recognized separate epitopes on the RBD and had distinctly different mechanisms of virus neutralization unique to VNARs. Structural and biochemical data suggest that VNARs would be effective therapeutic agents against emerging SARS-CoV-2 mutants, including the Delta variant, and coronaviruses across multiple phylogenetic lineages. This study highlights the utility of VNARs as effective therapeutics against coronaviruses and may serve as a critical milestone for nearing a paradigm shift of the greater biologic landscape.
Organizational Affiliation:
Elasmogen Ltd, Liberty Building Foresterhill Road, Aberdeen, AB25 2ZP, UK.