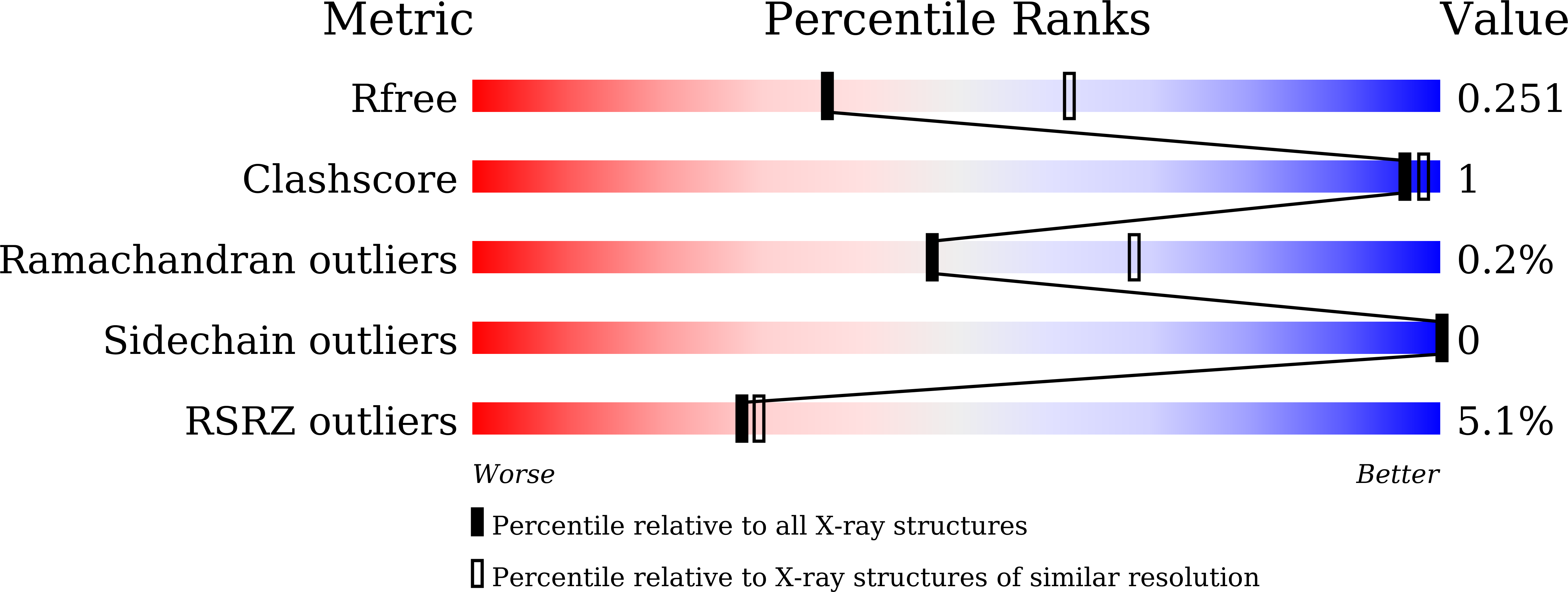
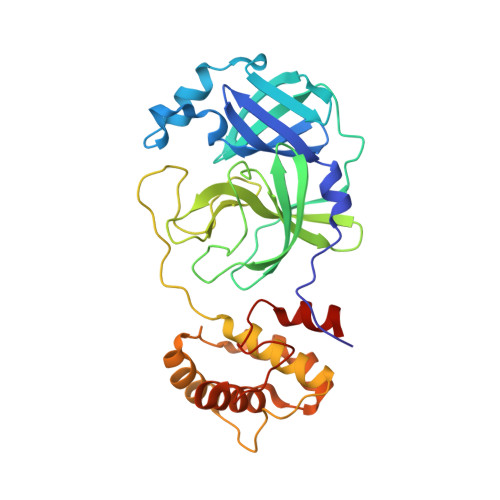
In silico screening-based discovery of novel covalent inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease.
Xiong, M., Nie, T., Shao, Q., Li, M., Su, H., Xu, Y.(2022) Eur J Med Chem 231: 114130-114130
- PubMed: 35114541
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114130
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7VVT - PubMed Abstract:
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) 3CL protease (3CL pro ) has been regarded as an extremely promising antiviral target for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Here, we carried out a virtual screening based on commercial compounds database to find novel covalent non-peptidomimetic inhibitors of this protease. It allowed us to identify 3 hit compounds with potential covalent binding modes, which were evaluated through an enzymatic activity assay of the SARS-CoV-2 3CL pro . Moreover, an X-ray crystal structure of the SARS-CoV-2 3CL pro in complex with compound 8, the most potent hit with an IC 50 value of 8.50 μM, confirmed the covalent binding of the predicted warhead to the catalytic residue C145, as well as portrayed interactions of the compound with S1' and S2 subsites at the ligand binding pocket. Overall, the present work not merely provided an experiment-validated covalent hit targeting the SARS-CoV-2 3CL pro , but also displayed a prime example to seeking new covalent small molecules by a feasible and effective computational approach.
Organizational Affiliation:
CAS Key Laboratory of Receptor Research and State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 201203, China; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049, China.