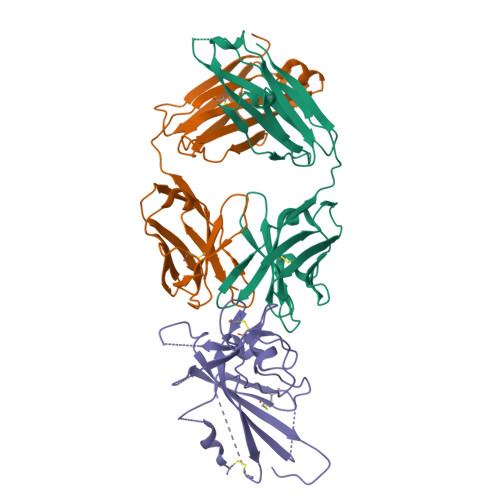
Cross-reaction of current available SARS-CoV-2 MAbs against the pangolin-origin coronavirus GX/P2V/2017.
Jia, Y., Niu, S., Hu, Y., Chai, Y., Zheng, A., Su, C., Wu, L., Han, P., Han, P., Lu, D., Liu, Z., Yan, X., Tian, D., Chen, Z., Qi, J., Tian, W.X., Wang, Q., Gao, G.F.(2022) Cell Rep 41: 111831-111831
- PubMed: 36493785
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111831
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7XNF, 7XSW - PubMed Abstract:
Since the identification of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the etiological agent of COVID-19, multiple SARS-CoV-2-related viruses have been characterized, including pangolin-origin GD/1/2019 and GX/P2V/2017. Our previous study indicated that both viruses have the potential to infect humans. Here, we find that CB6 (commercial name etesevimab), a COVID-19 therapeutic monoclonal antibody (MAb) developed by our group, efficiently inhibits GD/1/2019 but not GX/P2V/2017. A total of 50 SARS-CoV-2 MAbs divided into seven groups based on their receptor-binding domain (RBD) epitopes, together with the COVID-19 convalescent sera, are systematically screened for their cross-binding and cross-neutralizing properties against GX/P2V/2017. We find that GX/P2V/2017 displays substantial immune difference from SARS-CoV-2. Furthermore, we solve two complex structures of the GX/P2V/2017 RBD with MAbs belonging to RBD-1 and RBD-5, providing a structural basis for their different antigenicity. These results highlight the necessity for broad anti-coronavirus countermeasures and shed light on potential therapeutic targets.
Organizational Affiliation:
College of Veterinary Medicine, Shanxi Agricultural University, Jinzhong 030801, China; CAS Key Laboratory of Pathogen Microbiology and Immunology, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China.