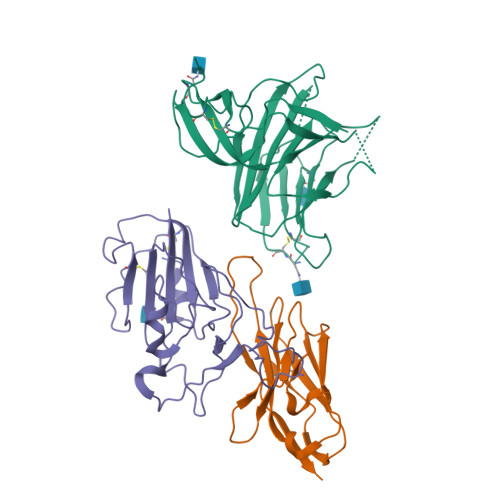
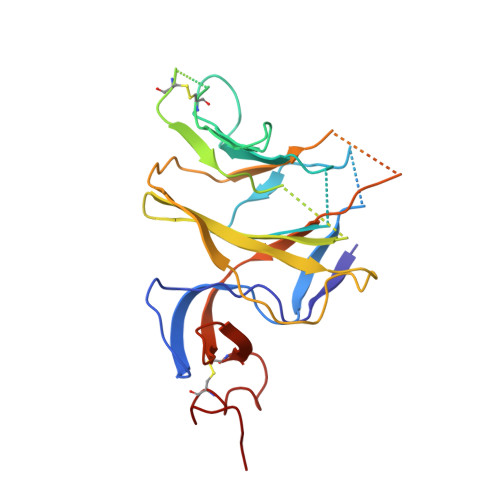
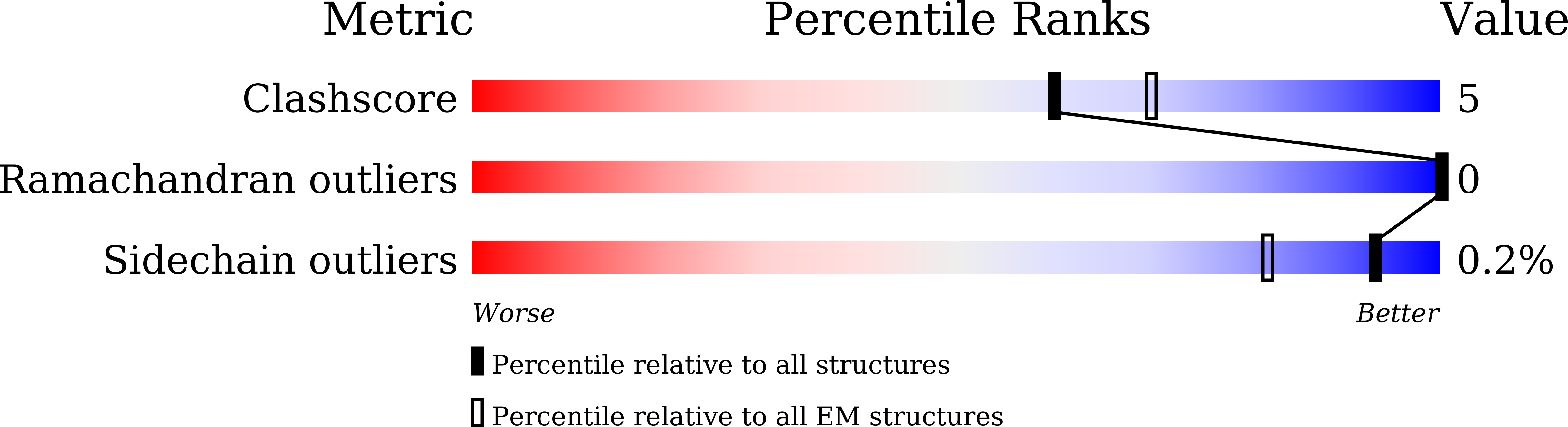A potent synthetic nanobody with broad-spectrum activity neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 virus and the Omicron variant BA.1 through a unique binding mode.
Zhao, D., Liu, L., Liu, X., Zhang, J., Yin, Y., Luan, L., Jiang, D., Yang, X., Li, L., Xiong, H., Xing, D., Zheng, Q., Xia, N., Tao, Y., Li, S., Huang, H.(2022) J Nanobiotechnology 20: 411-411
- PubMed: 36109732
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-022-01619-y
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7XRP - PubMed Abstract:
The major challenge to controlling the COVID pandemic is the rapid mutation rate of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, leading to the escape of the protection of vaccines and most of the neutralizing antibodies to date. Thus, it is essential to develop neutralizing antibodies with broad-spectrum activity targeting multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants. Here, we report a synthetic nanobody (named C5G2) obtained by phage display and subsequent antibody engineering. C5G2 has a single-digit nanomolar binding affinity to the RBD domain and inhibits its binding to ACE2 with an IC 50 of 3.7 nM. Pseudovirus assays indicated that monovalent C5G2 could protect the cells from infection with SARS-CoV-2 wild-type virus and most of the viruses of concern, i.e., Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Omicron variants. Strikingly, C5G2 has the highest potency against Omicron BA.1 among all the variants, with an IC 50 of 4.9 ng/mL. The cryo-EM structure of C5G2 in complex with the spike trimer showed that C5G2 binds to RBD mainly through its CDR3 at a conserved region that does not overlap with the ACE2 binding surface. Additionally, C5G2 binds simultaneously to the neighboring NTD domain of the spike trimer through the same CDR3 loop, which may further increase its potency against viral infection. Third, the steric hindrance caused by FR2 of C5G2 could inhibit the binding of ACE2 to RBD as well. Thus, this triple-function nanobody may serve as an effective drug for prophylaxis and therapy against Omicron as well as future variants.
Organizational Affiliation:
Qingdao Cancer Institute, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, 266071, China.