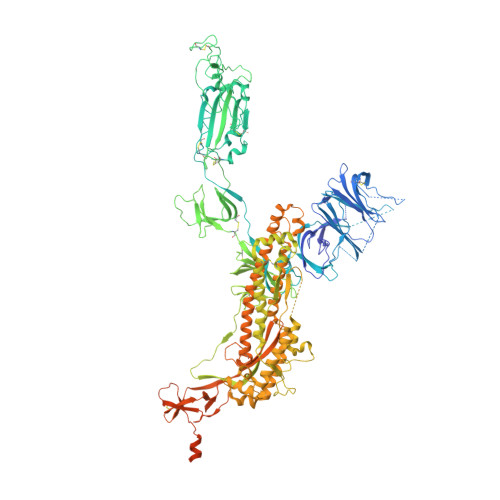
Structural Basis for the Enhanced Infectivity and Immune Evasion of Omicron Subvariants.
Li, Y., Shen, Y., Zhang, Y., Yan, R.(2023) Viruses 15
- PubMed: 37376697
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061398
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7Y1Y, 7Y1Z, 7Y20, 7Y21, 8I9E - PubMed Abstract:
The Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2 have emerged as the dominant strains worldwide, causing the COVID-19 pandemic. Each Omicron subvariant contains at least 30 mutations on the spike protein (S protein) compared to the original wild-type (WT) strain. Here we report the cryo-EM structures of the trimeric S proteins from the BA.1, BA.2, BA.3, and BA.4/BA.5 subvariants, with BA.4 and BA.5 sharing the same S protein mutations, each in complex with the surface receptor ACE2. All three receptor-binding domains of the S protein from BA.2 and BA.4/BA.5 are "up", while the BA.1 S protein has two "up" and one "down". The BA.3 S protein displays increased heterogeneity, with the majority in the all "up" RBD state. The different conformations preferences of the S protein are consistent with their varied transmissibility. By analyzing the position of the glycan modification on Asn343, which is located at the S309 epitopes, we have uncovered the underlying immune evasion mechanism of the Omicron subvariants. Our findings provide a molecular basis of high infectivity and immune evasion of Omicron subvariants, thereby offering insights into potential therapeutic interventions against SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Infectious Disease Research, Westlake Laboratory of Life Sciences and Biomedicine, Key Laboratory of Structural Biology of Zhejiang Province, School of Life Sciences, Westlake University, Hangzhou 310024, China.