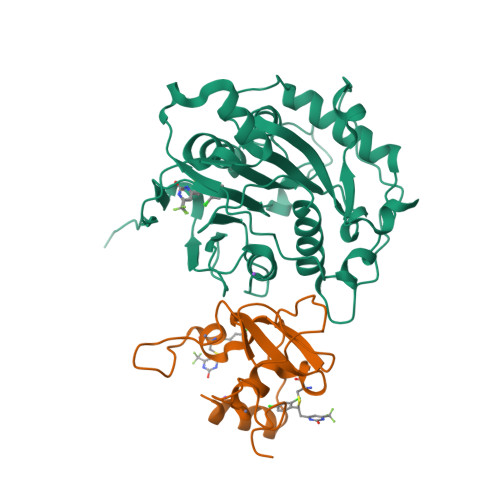
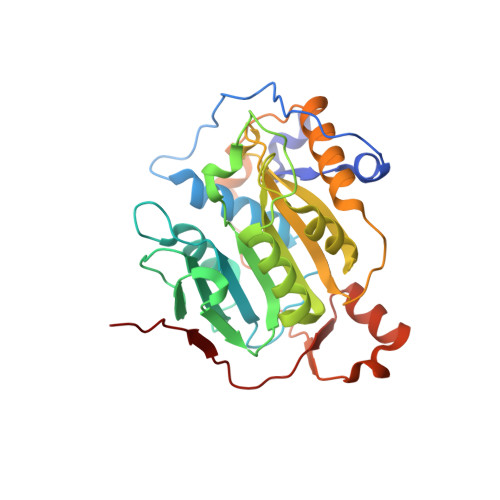
Discovery of a Druggable, Cryptic Pocket in SARS-CoV-2 nsp16 Using Allosteric Inhibitors.
Inniss, N.L., Kozic, J., Li, F., Rosas-Lemus, M., Minasov, G., Rybacek, J., Zhu, Y., Pohl, R., Shuvalova, L., Rulisek, L., Brunzelle, J.S., Bednarova, L., Stefek, M., Kormanik, J.M., Andris, E., Sebestik, J., Li, A.S.M., Brown, P.J., Schmitz, U., Saikatendu, K., Chang, E., Nencka, R., Vedadi, M., Satchell, K.J.F.(2023) ACS Infect Dis 9: 1918-1931
- PubMed: 37728236
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00203
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8F4S, 8F4Y - PubMed Abstract:
A collaborative, open-science team undertook discovery of novel small molecule inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 nsp16-nsp10 2'- O -methyltransferase using a high throughput screening approach with the potential to reveal new inhibition strategies. This screen yielded compound 5a , a ligand possessing an electron-deficient double bond, as an inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 nsp16 activity. Surprisingly, X-ray crystal structures revealed that 5a covalently binds within a previously unrecognized cryptic pocket near the S -adenosylmethionine binding cleft in a manner that prevents occupation by S -adenosylmethionine. Using a multidisciplinary approach, we examined the mechanism of binding of compound 5a to the nsp16 cryptic pocket and developed 5a derivatives that inhibited nsp16 activity and murine hepatitis virus replication in rat lung epithelial cells but proved cytotoxic to cell lines canonically used to examine SARS-CoV-2 infection. Our study reveals the druggability of this newly discovered SARS-CoV-2 nsp16 cryptic pocket, provides novel tool compounds to explore the site, and suggests a new approach for discovery of nsp16 inhibition-based pan-coronavirus therapeutics through structure-guided drug design.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Microbiology-Immunology and Center for Structural Biology of Infectious Diseases, Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, Illinois 60611, United States.