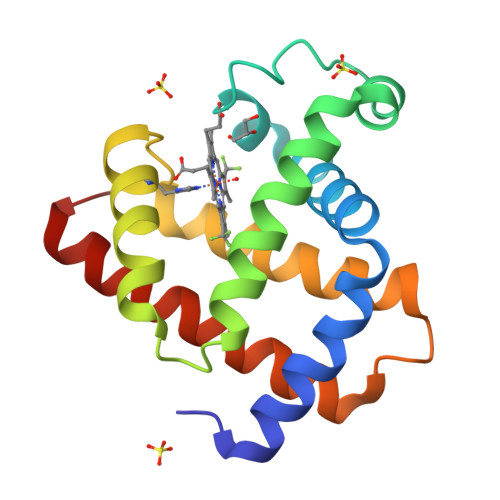
Redox Engineering of Myoglobin by Cofactor Substitution to Enhance Cyclopropanation Reactivity.
Kagawa, Y., Oohora, K., Himiyama, T., Suzuki, A., Hayashi, T.(2024) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 63: e202403485-e202403485
- PubMed: 38780472
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202403485
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8WF5 - PubMed Abstract:
Design of metal cofactor ligands is essential for controlling the reactivity of metalloenzymes. We investigated a carbene transfer reaction catalyzed by myoglobins containing iron porphyrin cofactors with one and two trifluoromethyl groups at peripheral sites (FePorCF3 and FePor(CF3)2, respectively), native heme and iron porphycene (FePc). These four myoglobins show a wide range of Fe(II)/Fe(III) redox potentials in the protein of +147 mV, +87 mV, +42 mV and -198 mV vs NHE, respectively. Myoglobin reconstituted with FePor(CF3)2 has a more positive potential which enhances the reactivity of a carbene intermediate with alkenes and demonstrates superior cyclopropanation of inert alkenes such as aliphatic and internal alkenes. In contrast, engineered myoglobin reconstituted with FePc has a more negative redox potential, which accelerates the formation of the intermediate but has low reactivity for inert alkenes. Mechanistic studies indicate that myoglobin with FePor(CF3)2 generates an undetectable active intermediate with a radical character. In contrast, this reaction catalyzed by myoglobin with FePc includes a detectable iron-carbene species with electrophilic character. This finding highlights the importance of redox-focused design of the iron porphyrinoid cofactor in hemoproteins to tune the reactivity of the carbene transfer reaction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Osaka University, Department of Applied Chemistry, JAPAN.