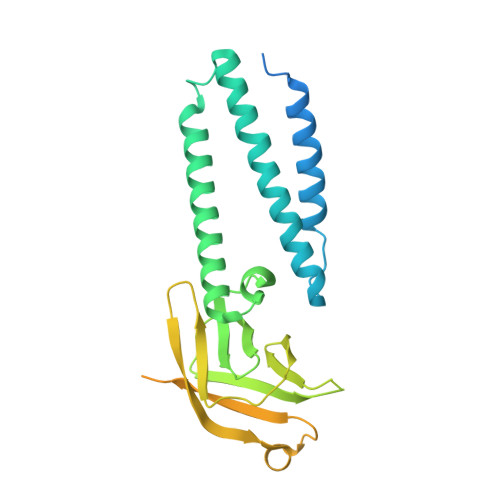
The SARS-CoV-2 accessory protein Orf3a is not an ion channel, but does interact with trafficking proteins.
Miller, A.N., Houlihan, P.R., Matamala, E., Cabezas-Bratesco, D., Lee, G.Y., Cristofori-Armstrong, B., Dilan, T.L., Sanchez-Martinez, S., Matthies, D., Yan, R., Yu, Z., Ren, D., Brauchi, S.E., Clapham, D.E.(2023) Elife 12
- PubMed: 36695574
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.84477
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8EQJ, 8EQS, 8EQT, 8EQU - PubMed Abstract:
The severe acute respiratory syndrome associated coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and SARS-CoV-1 accessory protein Orf3a colocalizes with markers of the plasma membrane, endocytic pathway, and Golgi apparatus. Some reports have led to annotation of both Orf3a proteins as viroporins. Here, we show that neither SARS-CoV-2 nor SARS-CoV-1 Orf3a form functional ion conducting pores and that the conductances measured are common contaminants in overexpression and with high levels of protein in reconstitution studies. Cryo-EM structures of both SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-1 Orf3a display a narrow constriction and the presence of a positively charged aqueous vestibule, which would not favor cation permeation. We observe enrichment of the late endosomal marker Rab7 upon SARS-CoV-2 Orf3a overexpression, and co-immunoprecipitation with VPS39. Interestingly, SARS-CoV-1 Orf3a does not cause the same cellular phenotype as SARS-CoV-2 Orf3a and does not interact with VPS39. To explain this difference, we find that a divergent, unstructured loop of SARS-CoV-2 Orf3a facilitates its binding with VPS39, a HOPS complex tethering protein involved in late endosome and autophagosome fusion with lysosomes. We suggest that the added loop enhances SARS-CoV-2 Orf3a's ability to co-opt host cellular trafficking mechanisms for viral exit or host immune evasion.
Organizational Affiliation:
Janelia Research Campus, Ashburn, United States.