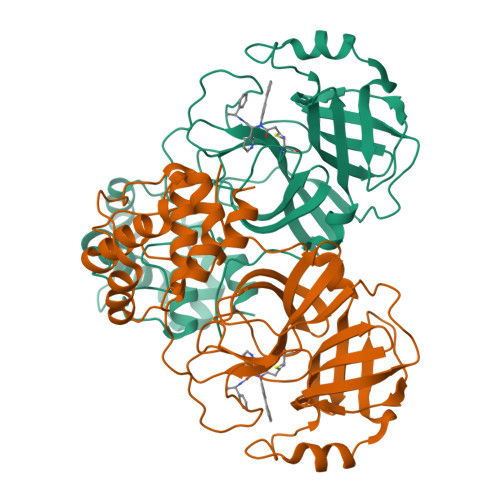
Exploring diverse reactive warheads for the design of SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors.
Tan, B., Sacco, M., Tan, H., Li, K., Joyce, R., Zhang, X., Chen, Y., Wang, J.(2023) Eur J Med Chem 259: 115667-115667
- PubMed: 37482021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115667
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8FIV, 8FIW - PubMed Abstract:
SARS-CoV-2 main protease (M pro ) is a validated antiviral drug target of nirmatrelvir, the active ingredient in Pfizer's oral drug Paxlovid. Drug-drug interactions limit the use of Paxlovid. In addition, drug-resistant M pro mutants against nirmatrelvir have been identified from cell culture viral passage and naturally occurring variants. As such, there is a need for a second generation of M pro inhibitors. In this study, we explored several reactive warheads in the design of M pro inhibitors. We identified Jun11119R (vinyl sulfonamide warhead), Jun10221R (propiolamide warhead), Jun1112R (4-chlorobut-2-ynamide warhead), Jun10541R (nitrile warhead), and Jun10963R (dually activated nitrile warhead) as potent M pro inhibitors. Jun10541R and Jun10963R also had potent antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 in Calu-3 cells with EC 50 values of 2.92 and 6.47 μM, respectively. X-ray crystal structures of M pro with Jun10541R and Jun10221 revealed covalent modification of Cys145. These M pro inhibitors with diverse reactive warheads collectively represent promising candidates for further development.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Medicinal Chemistry, Ernest Mario School of Pharmacy, Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, Piscataway, NJ, 08854, United States.