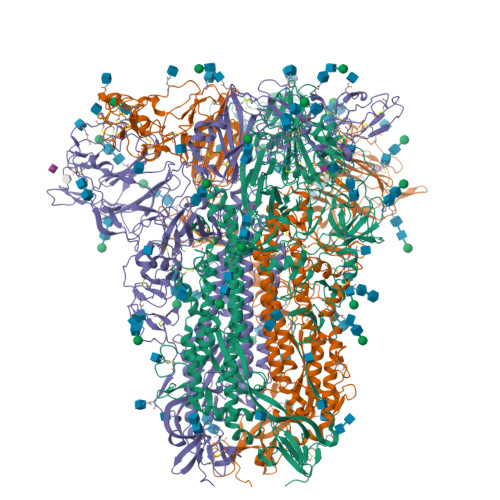
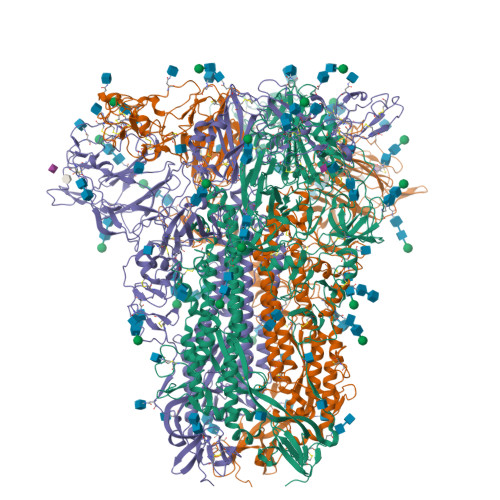
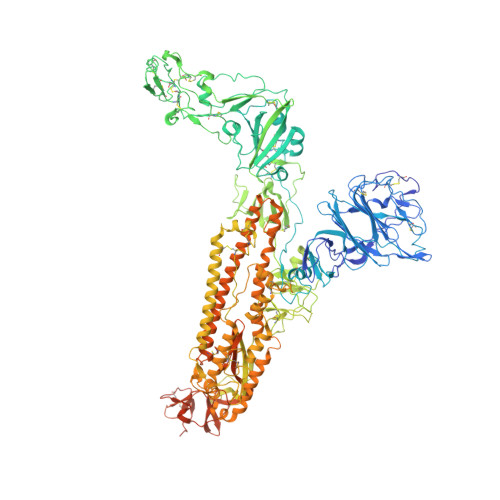
Sialoglycan binding triggers spike opening in a human coronavirus.
Pronker, M.F., Creutznacher, R., Drulyte, I., Hulswit, R.J.G., Li, Z., van Kuppeveld, F.J.M., Snijder, J., Lang, Y., Bosch, B.J., Boons, G.J., Frank, M., de Groot, R.J., Hurdiss, D.L.(2023) Nature 624: 201-206
- PubMed: 37794193
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06599-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8OHN, 8OPM, 8OPN, 8OPO - PubMed Abstract:
Coronavirus spike proteins mediate receptor binding and membrane fusion, making them prime targets for neutralizing antibodies. In the cases of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, spike proteins transition freely between open and closed conformations to balance host cell attachment and immune evasion 1-5 . Spike opening exposes domain S1 B , allowing it to bind to proteinaceous receptors 6,7 , and is also thought to enable protein refolding during membrane fusion 4,5 . However, with a single exception, the pre-fusion spike proteins of all other coronaviruses studied so far have been observed exclusively in the closed state. This raises the possibility of regulation, with spike proteins more commonly transitioning to open states in response to specific cues, rather than spontaneously. Here, using cryogenic electron microscopy and molecular dynamics simulations, we show that the spike protein of the common cold human coronavirus HKU1 undergoes local and long-range conformational changes after binding a sialoglycan-based primary receptor to domain S1 A . This binding triggers the transition of S1 B domains to the open state through allosteric interdomain crosstalk. Our findings provide detailed insight into coronavirus attachment, with possibilities of dual receptor usage and priming of entry as a means of immune escape.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biomolecular Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics, Bijvoet Center for Biomolecular Research, Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands.