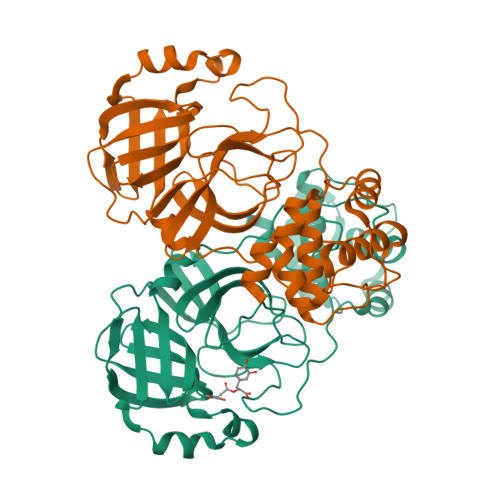
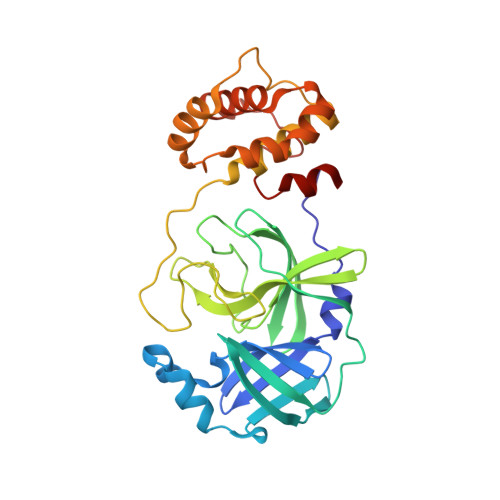
Structural basis of rosmarinic acid inhibitory mechanism on SARS-CoV-2 main protease.
Li, Q., Zhou, X., Wang, W., Xu, Q., Wang, Q., Li, J.(2024) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 724: 150230-150230
- PubMed: 38865813
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150230
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8YRH - PubMed Abstract:
The SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus is characterized by high mutation rates and significant infectivity, posing ongoing challenges for therapeutic intervention. To address potential challenges in the future, the continued development of effective drugs targeting SARS-CoV-2 remains an important task for the scientific as well as the pharmaceutical community. The main protease (M pro ) of SARS-CoV-2 is an ideal therapeutic target for COVID-19 drug development, leading to the introduction of various inhibitors, both covalent and non-covalent, each characterized by unique mechanisms of action and possessing inherent strengths and limitations. Natural products, being compounds naturally present in the environment, offer advantages such as low toxicity and diverse activities, presenting a viable source for antiviral drug development. Here, we identified a natural compound, rosmarinic acid, which exhibits significant inhibitory effects on the M pro of the SARS-CoV-2. Through detailed structural biology analysis, we elucidated the precise crystal structure of the complex formed between rosmarinic acid and SARS-CoV-2 M pro , revealing the molecular basis of its inhibitory mechanism. These findings not only enhance our understanding of the antiviral action of rosmarinic acid, but also provide valuable structural information and mechanistic insights for the further development of therapeutic strategies against SARS-CoV-2.
Organizational Affiliation:
Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 201800, China; Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049, China.