Structural insights into subunit-dependent functional regulation in epithelial sodium channels.
Houser, A., Baconguis, I.(2025) Structure 33: 349-362.e4
- PubMed: 39667931
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2024.11.013
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9BLR, 9BTG, 9BTU - PubMed Abstract:
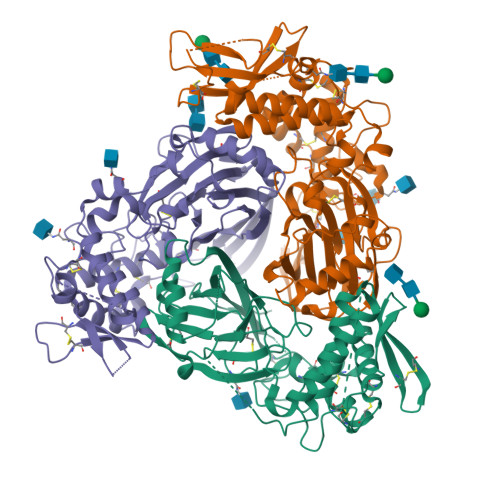
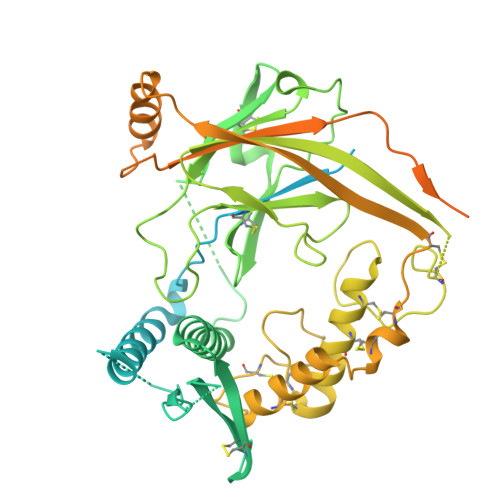
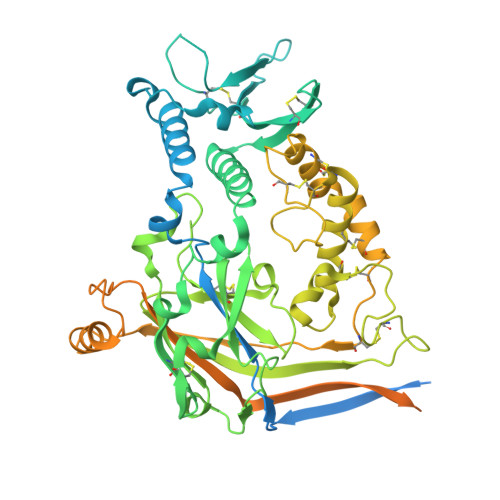
Epithelial sodium channels (ENaCs) play a crucial role in Na + reabsorption in mammals. To date, four subunits have been identified-α, β, γ, and δ-believed to form different heteromeric complexes. Currently, only the structure of the αβγ complex is known. To investigate the formation of channels with different subunit compositions and to determine how each subunit contributes to distinct channel properties, we co-expressed human δ, β, and γ. Using single-particle cryoelectron microscopy, we observed three distinct ENaC complexes. The structures unveil a pattern in which β and γ positions are conserved among the different complexes while the α position in αβγ trimer is occupied by either δ or another β. The δ subunit induces structural rearrangements in the γ subunit, which may contribute to the differences in channel activity between αβγ and δβγ channels. These structural changes provide molecular insights into how ENaC subunit composition modulates channel function.
Organizational Affiliation:
Neuroscience Graduate Program, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR 97239, USA.