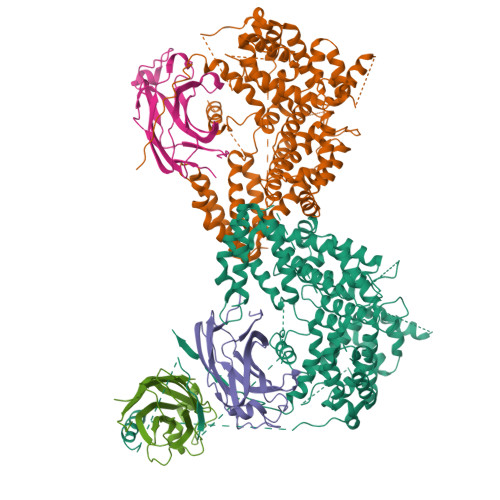
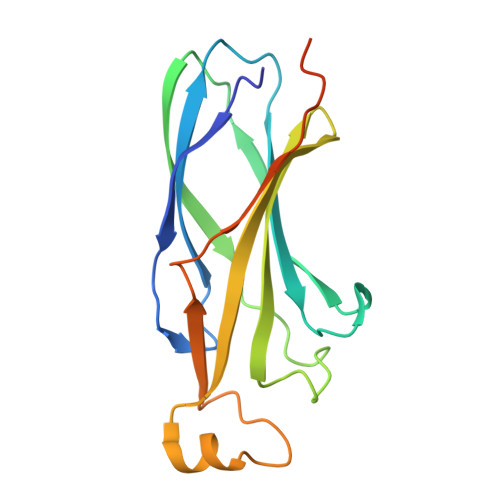
CODANIN-1 sequesters ASF1 by using a histone H3 mimic helix to regulate the histone supply.
Jeong, T.K., Frater, R.C.M., Yoon, J., Groth, A., Song, J.J.(2025) Nat Commun 16: 2181-2181
- PubMed: 40038274
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-56976-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9IMZ - PubMed Abstract:
ASF1 is a major histone chaperone that regulates the supply of histone H3-H4 and facilitates nucleosome assembly to maintain chromatin structure during DNA replication and transcription. CODANIN-1 negatively regulates the function of ASF1. However, the molecular mechanism by which CODANIN-1 inhibits the ASF1-mediated histone supply remains elusive. Here, we present the cryo-EM structure of a human CODANIN-1_ASF1A complex at 3.75 Å resolution. The structure reveals that CODANIN-1 forms a dimer where each monomer holds two ASF1 molecules, utilizing two B-domains and two histone H3 mimic helices (HMHs). The interaction of CODANIN-1 with ASF1 via the HMH and B-domains inhibits the formation of an ASF1/H3-H4 complex and sequesters ASF1 in the cytoplasm. Our study provides a structural and molecular basis for the function of CODANIN-1 as negative regulator that highjacks ASF1 interaction sites with histones and downstream chaperones to inhibit nucleosome assembly.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, KI for the BioCentury, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon, Korea.