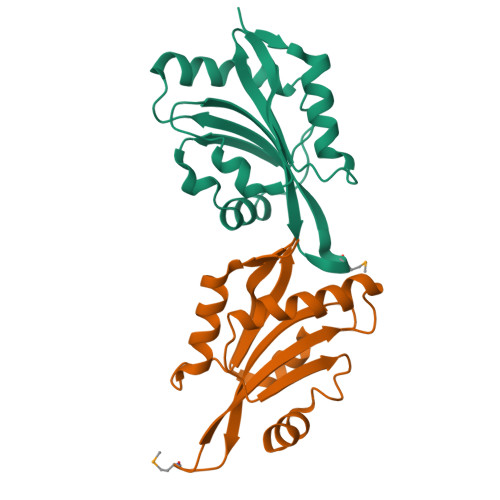
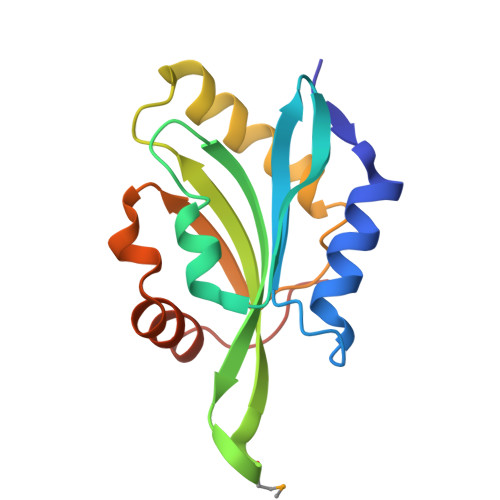
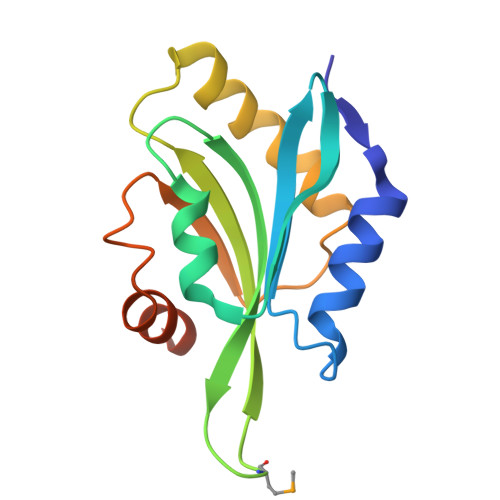
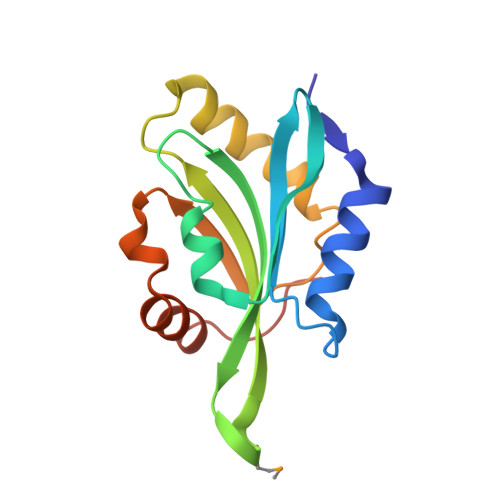
Crystal Structure of Human Coactosin-like Protein
Liu, L., Wei, Z., Wang, Y., Wan, M., Cheng, Z., Gong, W.(2004) J Mol Biology 344: 317-323
- PubMed: 15522287
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.09.036
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1T2L - PubMed Abstract:
Human coactosin-like protein is an actin filament binding protein but does not bind to globular actin. It associates with 5-Lipoxygenase both in vivo and in vitro, playing important roles in modulating the activities of actin and 5-Lipoxygenase. Coactosin counteracts the capping activity of capping protein which inhibits the actin polymerization. We determined the crystal structures of human coactosin-like protein by multi-wavelength anomalous dispersion method. The structure showed a high level of similarity to ADF-H domain, although their amino acid sequences share low degree of homology. A few conserved hydrophobic residues that may contribute to the folding were identified. This structure suggests coactosin-like protein bind to F-actin in a different way from ADF/Cofilin family. Combined with the information from previous mutagenesis studies, the binding sites for F-actin and 5-Lipoxygenase were analyzed, respectively. These two sites are quite close, which might prevent F-actin and 5-Lipoxygenase from binding to coactosin simultaneously.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, People's Republic of China.