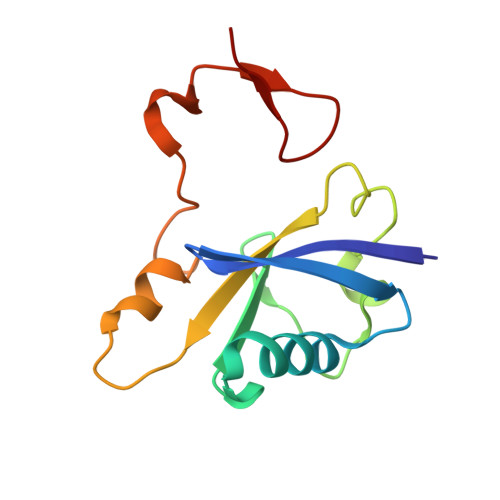
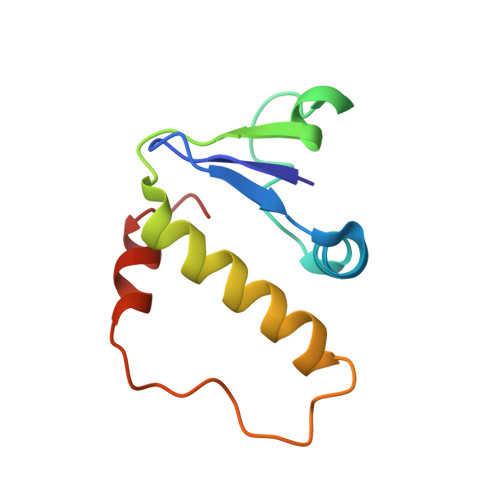
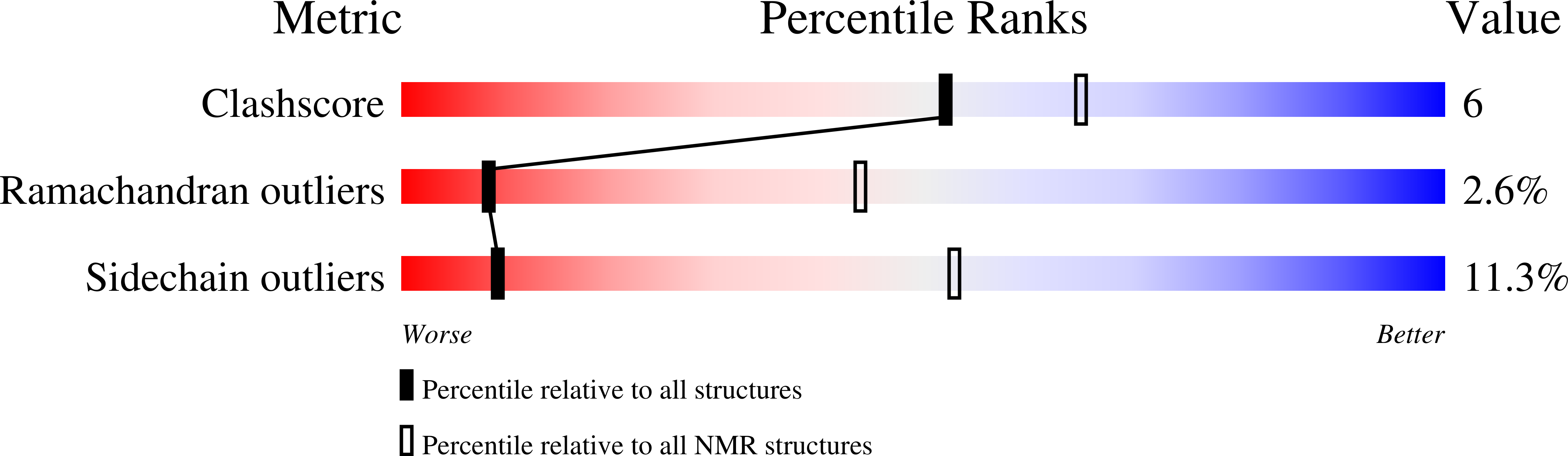Insight into the HIV-1 Vif SOCS-box-ElonginBC interaction.
Lu, Z., Bergeron, J.R., Atkinson, R.A., Schaller, T., Veselkov, D.A., Oregioni, A., Yang, Y., Matthews, S.J., Malim, M.H., Sanderson, M.R.(2013) Open Biol 3: 130100-130100
- PubMed: 24225024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1098/rsob.130100
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MA9 - PubMed Abstract:
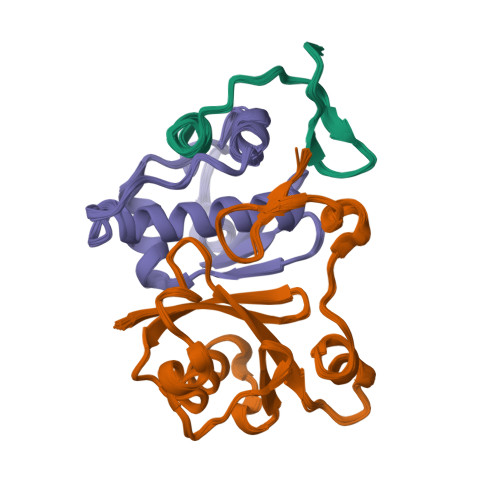
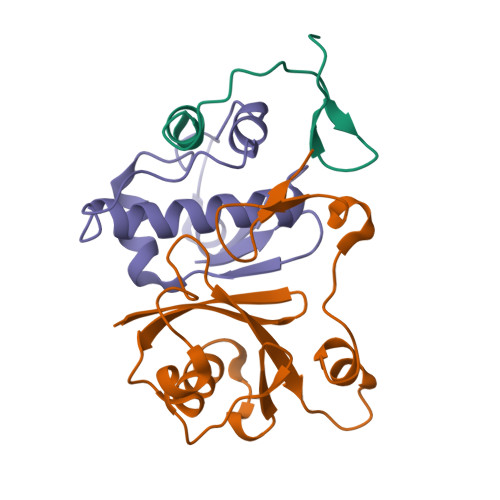
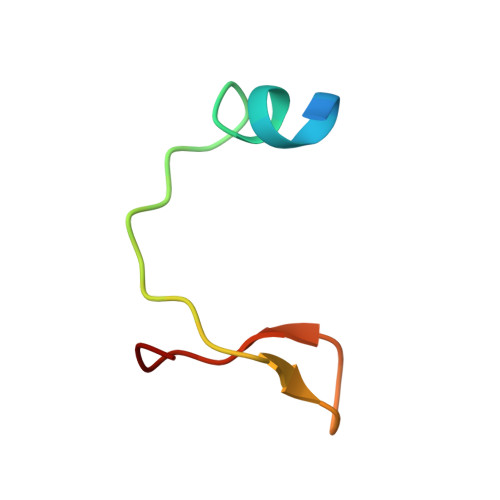
The HIV-1 viral infectivity factor (Vif) neutralizes cell-encoded antiviral APOBEC3 proteins by recruiting a cellular ElonginB (EloB)/ElonginC (EloC)/Cullin5-containing ubiquitin ligase complex, resulting in APOBEC3 ubiquitination and proteolysis. The suppressors-of-cytokine-signalling-like domain (SOCS-box) of HIV-1 Vif is essential for E3 ligase engagement, and contains a BC box as well as an unusual proline-rich motif. Here, we report the NMR solution structure of the Vif SOCS-ElonginBC (EloBC) complex. In contrast to SOCS-boxes described in other proteins, the HIV-1 Vif SOCS-box contains only one α-helical domain followed by a β-sheet fold. The SOCS-box of Vif binds primarily to EloC by hydrophobic interactions. The functionally essential proline-rich motif mediates a direct but weak interaction with residues 101-104 of EloB, inducing a conformational change from an unstructured state to a structured state. The structure of the complex and biophysical studies provide detailed insight into the function of Vif's proline-rich motif and reveal novel dynamic information on the Vif-EloBC interaction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Randall Division of Cell and Molecular Biophysics, King's College London, 3rd Floor, New Hunt's House, Guy's Campus, London Bridge, London SE1 1UL, UK.