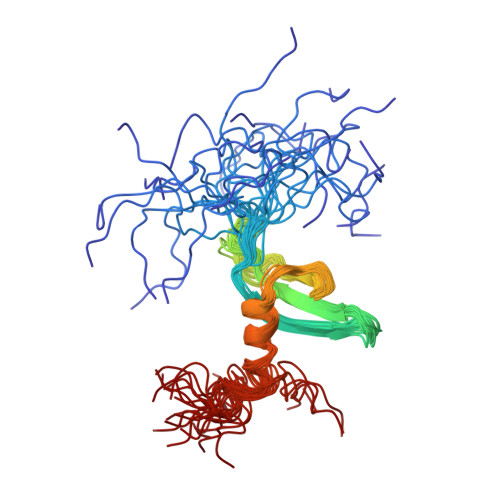
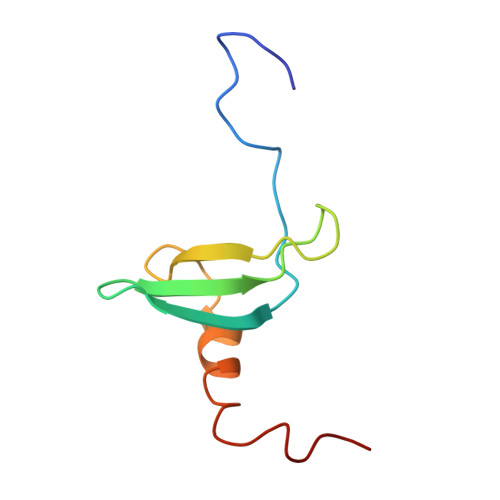
Structure of the chromatin binding (chromo) domain from mouse modifier protein 1.
Ball, L.J., Murzina, N.V., Broadhurst, R.W., Raine, A.R., Archer, S.J., Stott, F.J., Murzin, A.G., Singh, P.B., Domaille, P.J., Laue, E.D.(1997) EMBO J 16: 2473-2481
- PubMed: 9171360
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/16.9.2473
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1AP0 - PubMed Abstract:
The structure of a chromatin binding domain from mouse chromatin modifier protein 1 (MoMOD1) was determined using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The protein consists of an N-terminal three-stranded anti-parallel beta-sheet which folds against a C-terminal alpha-helix. The structure reveals an unexpected homology to two archaebacterial DNA binding proteins which are also involved in chromatin structure. Structural comparisons suggest that chromo domains, of which more than 40 are now known, act as protein interaction motifs and that the MoMOD1 protein acts as an adaptor mediating interactions between different proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Cambridge Centre for Molecular Recognition, Department of Biochemistry, University of Cambridge, UK.