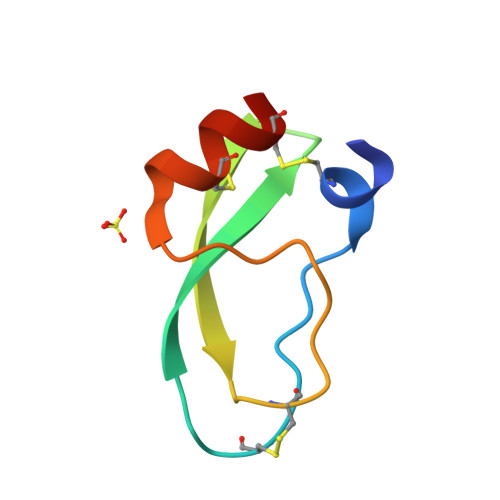
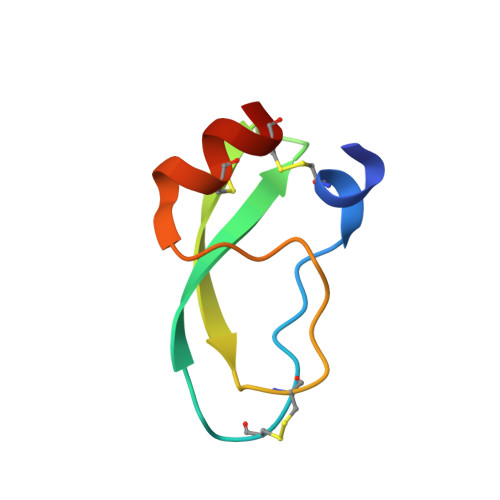
The 1.6 A structure of Kunitz-type domain from the alpha 3 chain of human type VI collagen.
Arnoux, B., Merigeau, K., Saludjian, P., Norris, F., Norris, K., Bjorn, S., Olsen, O., Petersen, L., Ducruix, A.(1995) J Mol Biology 246: 609-617
- PubMed: 7533217
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80110-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1KNT - PubMed Abstract:
The C-terminal Kunitz-type domain from the alpha 3 chain of human type VI collagen (C5), a single 58 amino acid residue chain with three disulfide bridges, was cloned, expressed and crystallized in a monoclonic form, space group P2(1), with a = 25.7 A, b = 38.2 A, c = 28.8 A and beta = 109 degrees. The structure was resolved by molecular replacement, using Alzheimer's protein precursor inhibitor and bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor three-dimensional structures as search models. The molecule with one sulfate ion and 43 associated water molecules was refined by XPLOR to an R-factor of 18.9% at 1.6 A. The molecule was not degraded by trypsin and did not inhibit trypsin or tested serine proteases. As opposed to the other Kunitz family members, C5 demonstrates left-handed chirality of the Cys14-Cys38 disulfide bond. Inversion of the Thr13 carbonyl and bulky side-chains at the interface with trypsin in a model of the C5-trypsin complex may explain the lack of inhibition of trypsin.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratoire de Biologie Structurale, CNRS, Gif sur Yvette, France.