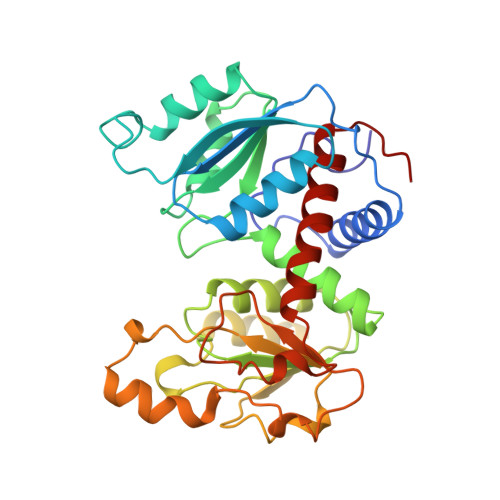
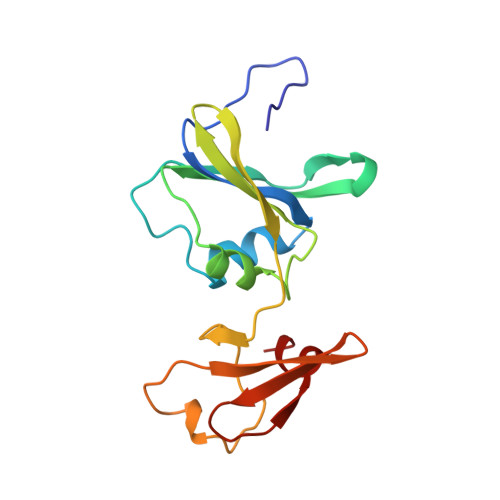
A single mutation in the regulatory chain of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase results in an extreme T-state structure.
Williams, M.K., Stec, B., Kantrowitz, E.R.(1998) J Mol Biol 281: 121-134
- PubMed: 9680480
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1998.1923
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1NBE - PubMed Abstract:
Kinetic analysis of a mutant version of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase in which Thr82 in the regulatory chain (Thr82r) was replaced by Ala results in a shift in the T <==> R equilibrium towards the T-state. In order to understand the structural determinants of this T-state stabilization, the X-ray structure of the unliganded Thr82r-->Ala enzyme was determined at 2. 6 A resolution and refined to a crystallographic residual of 0.175. The structure of the mutant r1 regulatory chain is more similar to that of the r6 regulatory chain than observed for the wild-type enzyme, resulting in a more symmetric structure. Furthermore, the structural changes in the mutant enzyme appears to occur only in the r1 chain, while the r6 chain is almost identical in structure to that of the r6 chain of the wild-type enzyme. The structure of the mutant enzyme exhibits alterations in the subunit interfaces between the regulatory and catalytic chains, as well as in the interface between the allosteric and zinc domains within the regulatory chain. Moreover, the regulatory dimers are rotated around their respective 2-fold axes approximately 1 degrees beyond the rotation which occurs in the wild-type T-state enzyme. The structural analysis indicates that the enzyme is an "extreme" T-state, in which a larger rotation of the regulatory dimers is required for the T to R transition compared to the wild-type enzyme. This extreme T-state structure correlates well with the kinetic parameters determined for the mutant enzyme, showing a stabilized T-state. Furthermore, the structural analysis of the mutant enzyme suggests that replacement of Thr82r with Ala alters the local conformation of the nucleotide binding pocket and therefore offers a plausible explanation for the reduced affinity of the enzyme for nucleotides.
Organizational Affiliation:
Merkert Chemistry Center, Boston College, Chestnut Hill, MA 02167, USA.