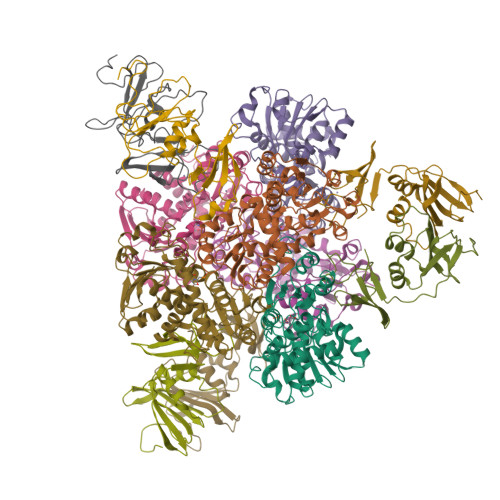
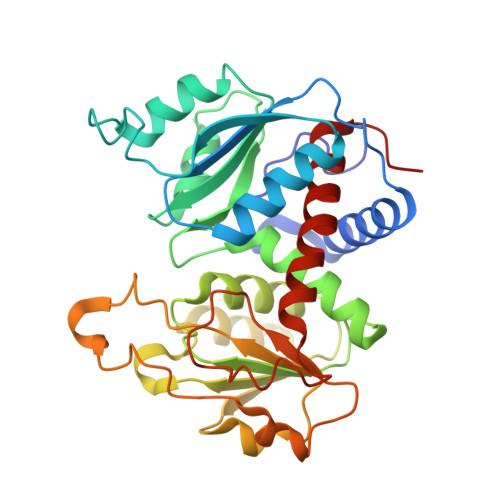
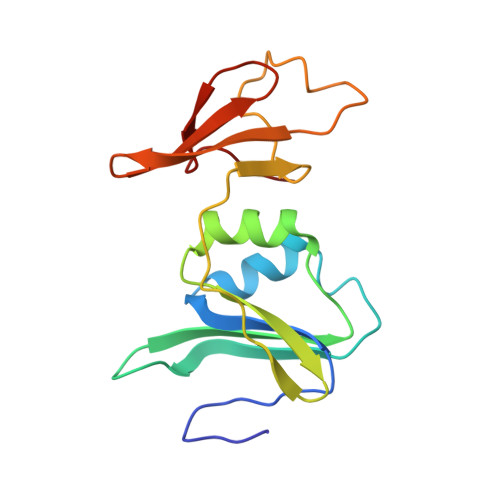
Aspartate Transcarbamylase (ATCase) of Escherichia coli: A New Crystalline R-State Bound to PALA, or to Product Analogues Citrate and Phosphate
Huang, J., Lipscomb, W.N.(2004) Biochemistry 43: 6415-6421
- PubMed: 15157075
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi030213b
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1Q95, 1R0B - PubMed Abstract:
Structures of the R-state of Escherichia coli ATCase maintained with carbamyl phosphate and succinate, phosphonoacetamide and malonate, or N-phosphonacetyl-l-aspartate (PALA) have previously been made in the space group P321, in which the two independent r (regulatory) and two independent c (catalytic) chains are repeated by crystallographic symmetry to yield the holoenzyme c(6)r(6), ((c(3))(2)(r(2))(3)). The exploration of a new crystalline R-state P2(1)2(1)2(1) was undertaken to examine the c(3).c(3) expansion of 11 A in the T-to-R transition, and to further test whether intermolecular contacts influence the binding of PALA. The results show that the expansion along the 3-fold axis is 10 A, and that the binding modes of the six crystallographic independent PALA molecules are virtually identical to one another, and to modes described previously. As further test, the PALA, a bisubstrate analogue, was displaced by citrate and phosphate, where citrate is an analogue of product carbamylaspartate. The results support the conclusions about the binding of the three previously studied analogues, and further support, within about 0.5 A, the structure proposed for the transition state [Gouaux, J. E., Krause, K. L., and Lipscomb, W. N. (1987) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 142, 893-897; Jin, L., Stec, B., Lipscomb, W. N., and Kantrowitz, E. R. (1999) Proteins: Struct., Funct., Genet. 37, 729-742].
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard University, 12 Oxford Street, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02138, USA.