Avidin Related Protein 2 Shows Unique Structural and Functional Features Among the Avidin Protein Family.
Hytonen, V.P., Maatta, J.A., Kidron, H., Halling, K.K., Horha, J., Kulomaa, T., Nyholm, T.K.M., Johnson, M.S., Salminen, T.A., Kulomaa, M.S., Airenne, T.T.(2005) BMC Biotechnol 5: 28
- PubMed: 16212654
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-5-28
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WBI - PubMed Abstract:
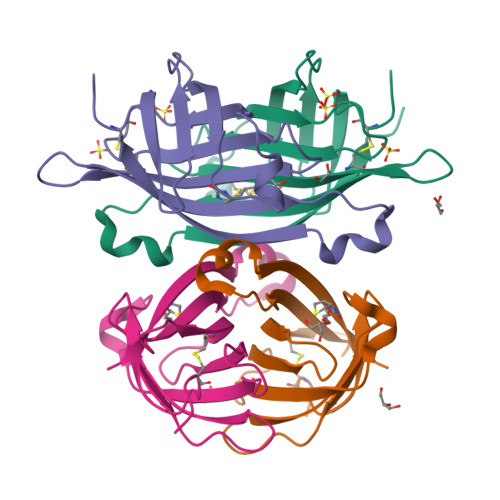
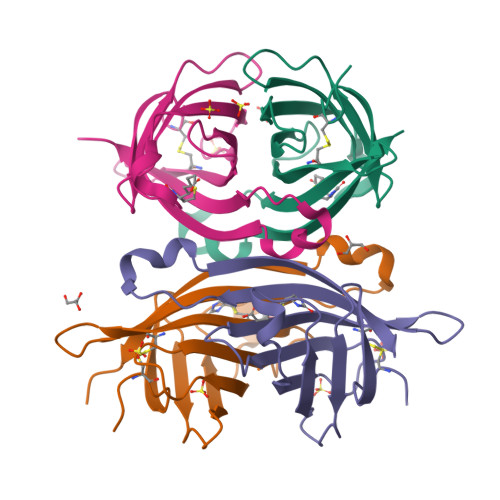
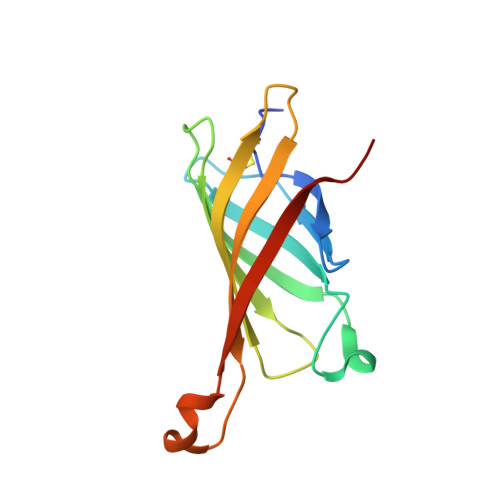
The chicken avidin gene family consists of avidin and several avidin related genes (AVRs). Of these gene products, avidin is the best characterized and is known for its extremely high affinity for D-biotin, a property that is utilized in numerous modern life science applications. Recently, the AVR genes have been expressed as recombinant proteins, which have shown different biotin-binding properties as compared to avidin. In the present study, we have employed multiple biochemical methods to better understand the structure-function relationship of AVR proteins focusing on AVR2. Firstly, we have solved the high-resolution crystal structure of AVR2 in complex with a bound ligand, D-biotin. The AVR2 structure reveals an overall fold similar to the previously determined structures of avidin and AVR4. Major differences are seen, especially at the 1-3 subunit interface, which is stabilized mainly by polar interactions in the case of AVR2 but by hydrophobic interactions in the case of AVR4 and avidin, and in the vicinity of the biotin binding pocket. Secondly, mutagenesis, competitive dissociation analysis and differential scanning calorimetry were used to compare and study the biotin-binding properties as well as the thermal stability of AVRs and avidin. These analyses pinpointed the importance of residue 109 for biotin binding and stability of AVRs. The I109K mutation increased the biotin-binding affinity of AVR2, whereas the K109I mutation decreased the biotin-binding affinity of AVR4. Furthermore, the thermal stability of AVR2(I109K) increased in comparison to the wild-type protein and the K109I mutation led to a decrease in the thermal stability of AVR4. Altogether, this study broadens our understanding of the structural features determining the ligand-binding affinities and stability as well as the molecular evolution within the protein family. This novel information can be applied to further develop and improve the tools already widely used in avidin-biotin technology.
Organizational Affiliation:
NanoScience Center, Department of Biological and Environmental Science, University of Jyväskylä, P.O. Box 35 (YAB), FI-40014, Finland. veshyto@bytl.jyu.fi