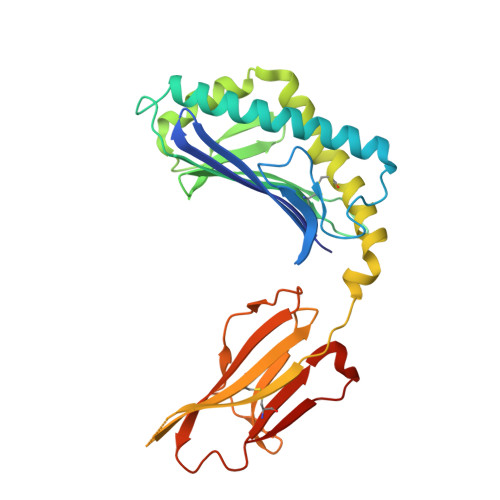
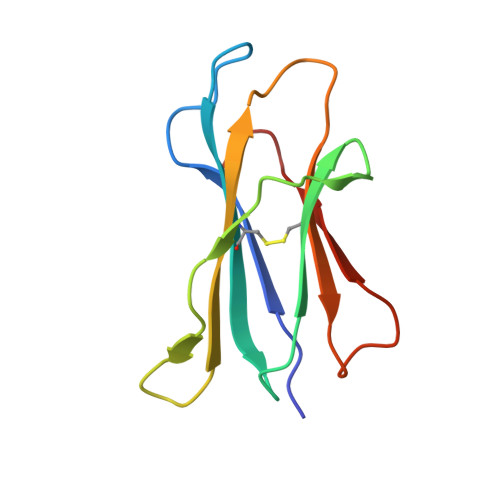
Structural basis for CD1d presentation of a sulfatide derived from myelin and its implications for autoimmunity
Zajonc, D.M., Maricic, I., Wu, D., Halder, R., Roy, K., Wong, C.-H., Kumar, V., Wilson, I.A.(2005) J Exp Med 202: 1517-1526
- PubMed: 16314439
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20051625
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2AKR - PubMed Abstract:
Sulfatide derived from the myelin stimulates a distinct population of CD1d-restricted natural killer T (NKT) cells. Cis-tetracosenoyl sulfatide is one of the immunodominant species in myelin as identified by proliferation, cytokine secretion, and CD1d tetramer staining. The crystal structure of mouse CD1d in complex with cis-tetracosenoyl sulfatide at 1.9 A resolution reveals that the longer cis-tetracosenoyl fatty acid chain fully occupies the A' pocket of the CD1d binding groove, whereas the sphingosine chain fills up the F' pocket. A precise hydrogen bond network in the center of the binding groove orients and positions the ceramide backbone for insertion of the lipid tails in their respective pockets. The 3'-sulfated galactose headgroup is highly exposed for presentation to the T cell receptor and projects up and away from the binding pocket due to its beta linkage, compared with the more intimate binding of the alpha-glactosyl ceramide headgroup to CD1d. These structure and binding data on sulfatide presentation by CD1d have important implications for the design of therapeutics that target T cells reactive for myelin glycolipids in autoimmune diseases of the central nervous system.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA.