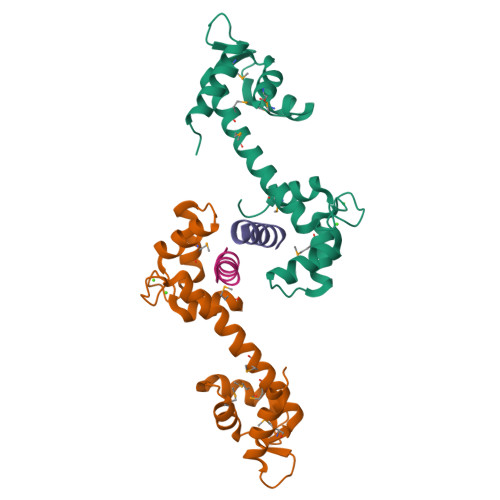
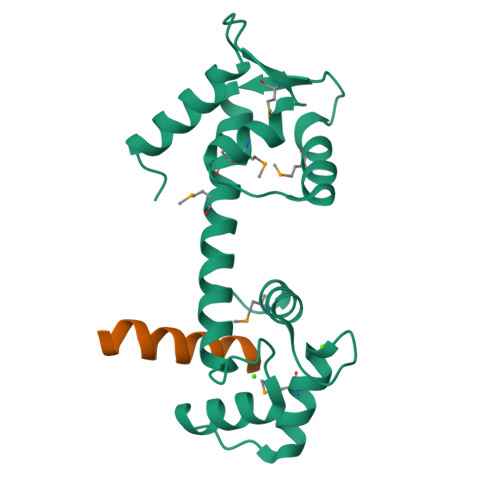
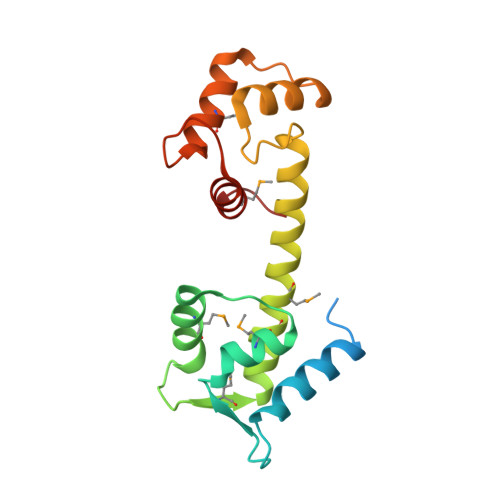
The structure of the human centrin 2-xeroderma pigmentosum group C protein complex.
Thompson, J.R., Ryan, Z.C., Salisbury, J.L., Kumar, R.(2006) J Biological Chem 281: 18746-18752
- PubMed: 16627479
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M513667200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2GGM - PubMed Abstract:
Human centrin-2 plays a key role in centrosome function and stimulates nucleotide excision repair by binding to the xeroderma pigmentosum group C protein. To determine the structure of human centrin-2 and to develop an understanding of molecular interactions between centrin and xeroderma pigmentosum group C protein, we characterized the crystal structure of calcium-loaded full-length centrin-2 complexed with a xeroderma pigmentosum group C peptide. Our structure shows that the carboxyl-terminal domain of centrin-2 binds this peptide and two calcium atoms, whereas the amino-terminal lobe is in a closed conformation positioned distantly by an ordered alpha-helical linker. A stretch of the amino-terminal domain unique to centrins appears disordered. Two xeroderma pigmentosum group C peptides both bound to centrin-2 also interact to form an alpha-helical coiled-coil. The interface between centrin-2 and each peptide is predominantly nonpolar, and key hydrophobic residues of XPC have been identified that lead us to propose a novel binding motif for centrin.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Physiology, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, Rochester, Minnesota 55905, USA. thompson.james@mayo.edu