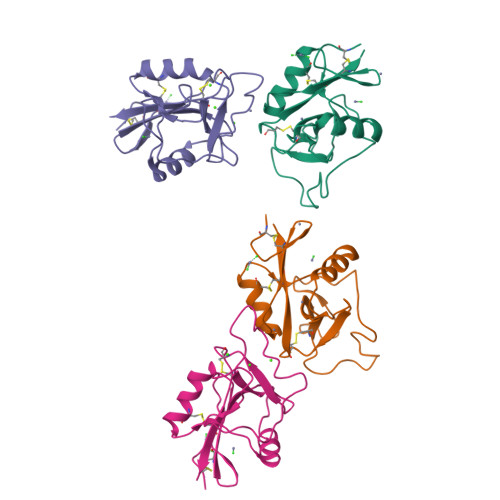
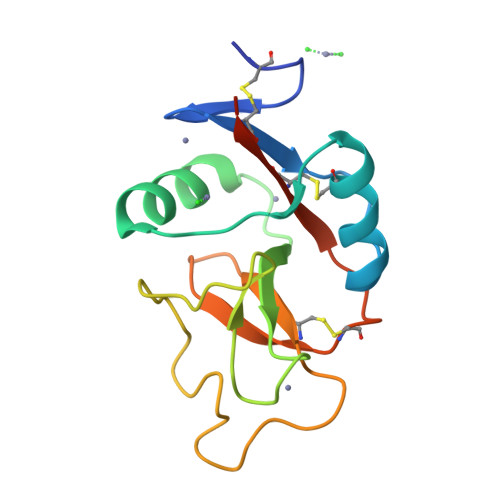
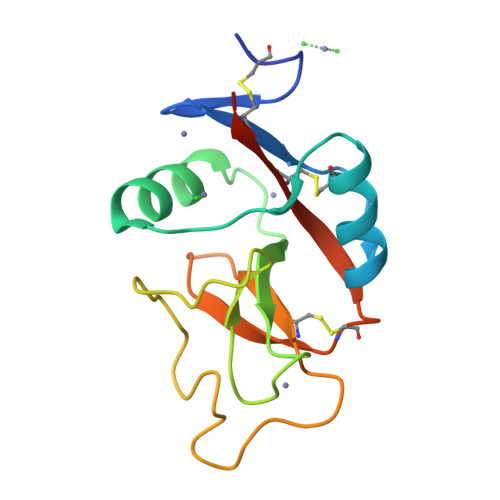
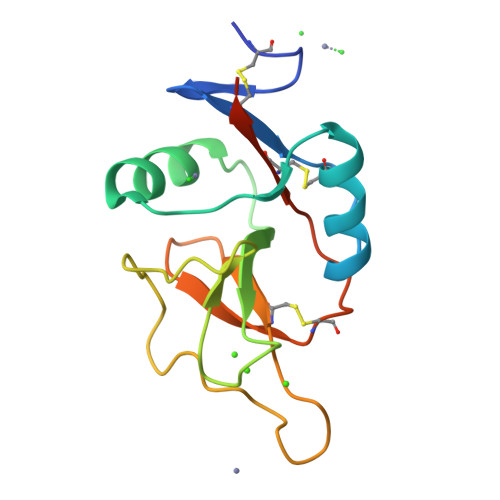
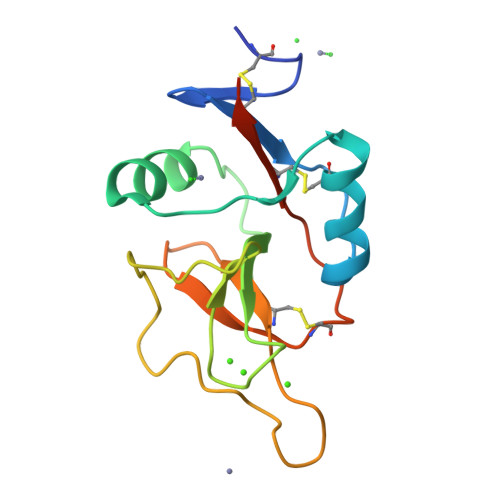
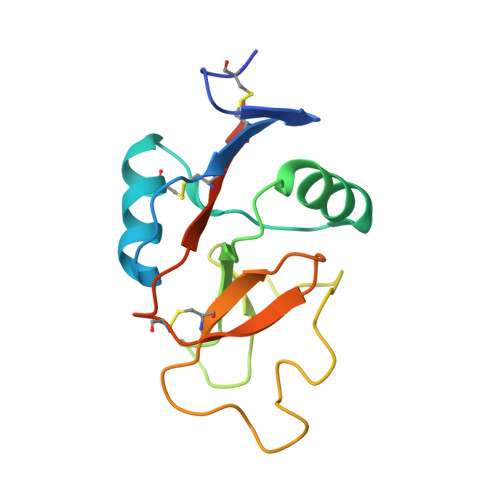
Scavenger receptor C-type lectin binds to the leukocyte cell surface glycan Lewis(x) by a novel mechanism.
Feinberg, H., Taylor, M.E., Weis, W.I.(2007) J Biological Chem 282: 17250-17258
- PubMed: 17420244
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M701624200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2OX8, 2OX9 - PubMed Abstract:
The scavenger receptor C-type lectin (SRCL) is unique in the family of class A scavenger receptors, because in addition to binding sites for oxidized lipoproteins it also contains a C-type carbohydrate-recognition domain (CRD) that interacts with specific glycans. Both human and mouse SRCL are highly specific for the Lewis(x) trisaccharide, which is commonly found on the surfaces of leukocytes and some tumor cells. Structural analysis of the CRD of mouse SRCL in complex with Lewis(x) and mutagenesis show the basis for this specificity. The interaction between mouse SRCL and Lewis(x) is analogous to the way that selectins and DC-SIGN bind to related fucosylated glycans, but the mechanism of the interaction is novel, because it is based on a primary galactose-binding site similar to the binding site in the asialoglycoprotein receptor. Crystals of the human receptor lacking bound calcium ions reveal an alternative conformation in which a glycan ligand would be released during receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structural Biology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California 94306, USA.