Biochemical and Structural Characterization of the Paralogous Benzoate Coa Ligases from Burkholderia Xenovorans Lb400: Defining the Entry Point Into the Novel Benzoate Oxidation (Box) Pathway.
Bains, J., Boulanger, M.J.(2007) J Mol Biology 373: 965
- PubMed: 17884091
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.08.008
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2V7B - PubMed Abstract:
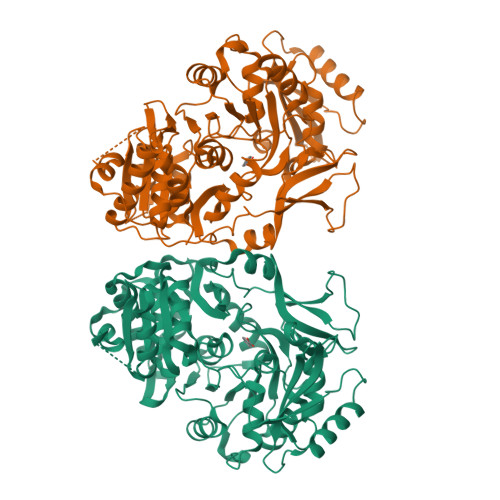
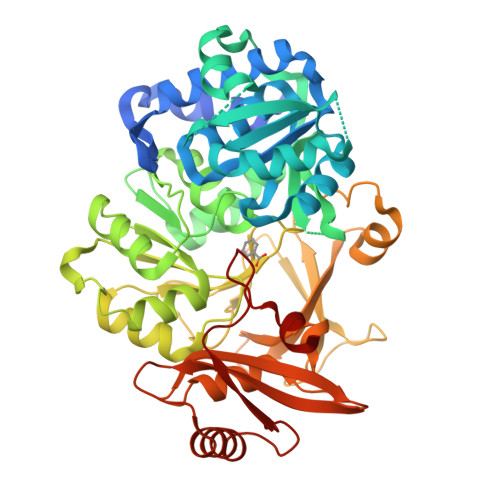
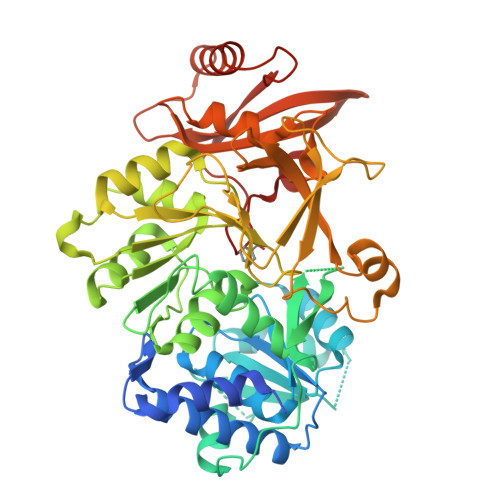
Xenobiotic aromatic compounds represent one of the most significant classes of environmental pollutants. A novel benzoate oxidation (box) pathway has been identified recently in Burkholderia xenovorans LB400 (referred to simply as LB400) that is capable of assimilating benzoate and intimately tied to the degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). The box pathway in LB400 is present in two paralogous copies (boxM and boxC) and encodes eight enzymes with the first committed step catalyzed by benzoate CoA ligase (BCL). As a first step towards delineating the biochemical role of the box pathway in LB400, we have carried out functional studies of the paralogous BCL enzymes (BCLM and BCLC) with 20 different putative substrates. We have established a structural rationale for the observed substrate specificities on the basis of a 1.84 A crystal structure of BCLM in complex with benzoate. These data show that, while BCLM and BCLC display similar overall substrate specificities, BCLM is significantly more active towards benzoate and 2-aminobenzoate with tighter binding (Km) and a faster reaction rate (Vmax). Despite these clear functional differences, the residues that define the substrate-binding site in BCLM are completely conserved in BCLC, suggesting that second shell residues may play a significant role in substrate recognition and catalysis. Furthermore, comparison of the active site of BCLM with the recently solved structures of 4-chlorobenzoate CoA ligase and 2, 3-dihydroxybenzoate CoA ligase offers additional insight into the molecular features that mediate substrate binding in adenylate-forming enzymes. This study provides the first biochemical characterization of a Box enzyme from LB400 and the first structural characterization of a Box enzyme from any organism, and further substantiates the concept of distinct roles for the two paralogous box pathways in LB400.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Microbiology, University of Victoria, PO Box 3055 STN CSC, Victoria, BC, Canada V8W 3P6.