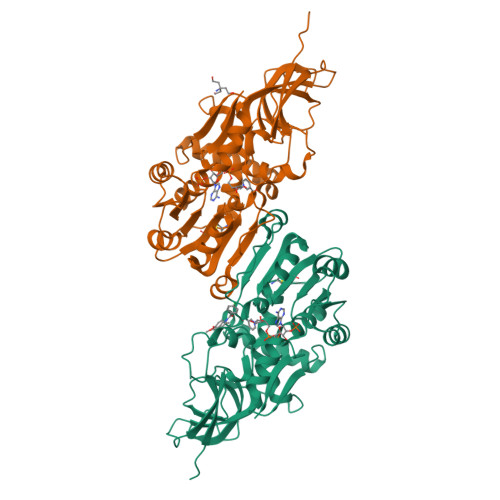
Crystal structure of anti-configuration of indomethacin and leukotriene B4 12-hydroxydehydrogenase/15-oxo-prostaglandin 13-reductase complex reveals the structural basis of broad spectrum indomethacin efficacy
Hori, T., Ishijima, J., Yokomizo, T., Ago, H., Shimizu, T., Miyano, M.(2006) J Biochem 140: 457-466
- PubMed: 16916844
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvj176
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2DM6 - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of the ternary complex of leukotriene B4 12-hydroxydehydrogenase/15-oxo-prostaglandin (15-oxo-PG) 13-reductase (LTB4 12HD/PGR), an essential enzyme for eicosanoid inactivation pathways, with indomethacin and NADP+ has been solved. An indomethacin molecule bound in the anti-configuration at one of the two active site clefts of the homo-dimer interface in the LTB4 12HD/PGR and was confirmed by a binding calorimetry. The chlorobenzene ring is buried in the hydrophobic pore used as a binding site by the omega-chain of 15-oxo-PGE2. The carboxyl group interacts with the guanidino group of Arg56 and the phenolic hydroxyl group of Tyr262. Indomethacin shows a broad spectrum of efficacy against lipid-mediator related proteins including cyclooxygenase-2, phospholipase A2, PGF synthase and PGE synthase-2 but in the syn-configuration as well as LTB4 12HD/PGR in the anti-configuration. Indomethacin does not necessarily mimic the binding mode of the lipid-mediator substrates in the active sites of these complex structures. Thus, the broad spectrum of indomethacin efficacy can be attributed to its ability to adopt a range of different stable conformations. This allows the indomethacin to adapt to the distinct binding site features of each protein whilst maintaining favorable interactions between the carboxyl group and a counter charged functional group.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biophysics Laboratory, RIKEN SPring-8 Center, Harima Institute, 1-1-1 Kouto, Sayo-cho, Sayo-gun, Hyogo 679-5148.