Structural basis for an inositol pyrophosphate kinase surmounting phosphate crowding.
Wang, H., Falck, J.R., Hall, T.M., Shears, S.B.(2011) Nat Chem Biol 8: 111-116
- PubMed: 22119861
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.733
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
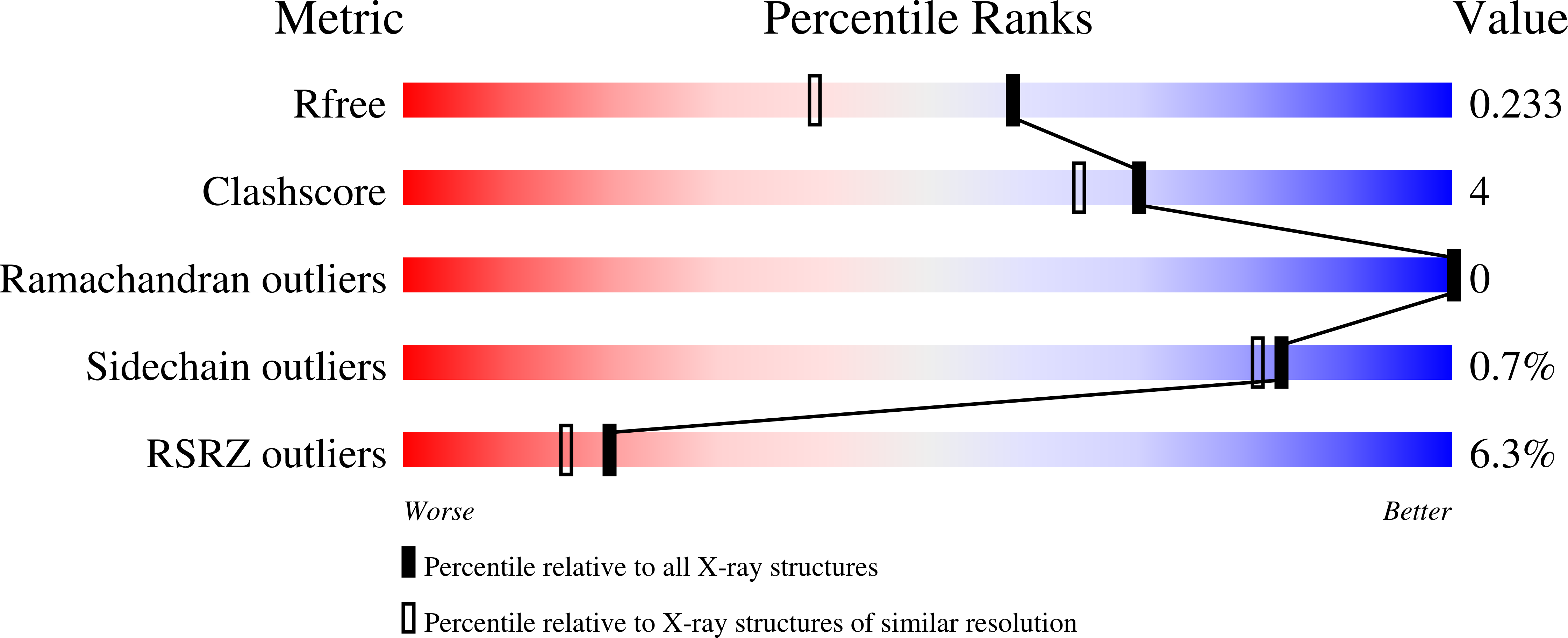
3T54, 3T7A, 3T99, 3T9A, 3T9B, 3T9C, 3T9D, 3T9E, 3T9F - PubMed Abstract:
Inositol pyrophosphates (such as IP7 and IP8) are multifunctional signaling molecules that regulate diverse cellular activities. Inositol pyrophosphates have 'high-energy' phosphoanhydride bonds, so their enzymatic synthesis requires that a substantial energy barrier to the transition state be overcome. Additionally, inositol pyrophosphate kinases can show stringent ligand specificity, despite the need to accommodate the steric bulk and intense electronegativity of nature's most concentrated three-dimensional array of phosphate groups. Here we examine how these catalytic challenges are met by describing the structure and reaction cycle of an inositol pyrophosphate kinase at the atomic level. We obtained crystal structures of the kinase domain of human PPIP5K2 complexed with nucleotide cofactors and either substrates, product or a MgF(3)(-) transition-state mimic. We describe the enzyme's conformational dynamics, its unprecedented topological presentation of nucleotide and inositol phosphate, and the charge balance that facilitates partly associative in-line phosphoryl transfer.
Organizational Affiliation:
Inositol Signaling Group, Laboratory of Signal Transduction, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health, Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, USA. wangh7@niehs.nih.gov