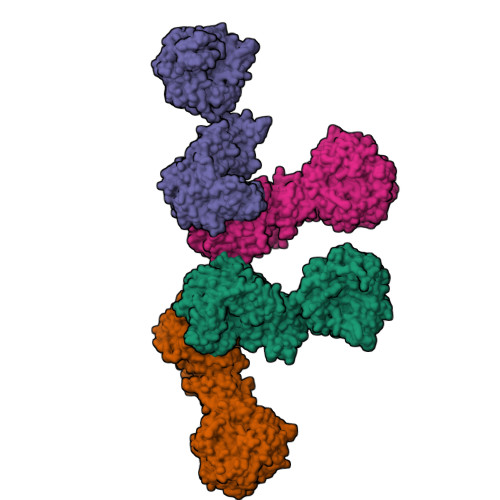
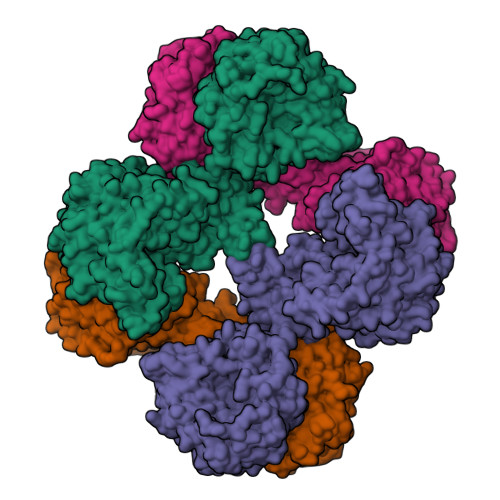
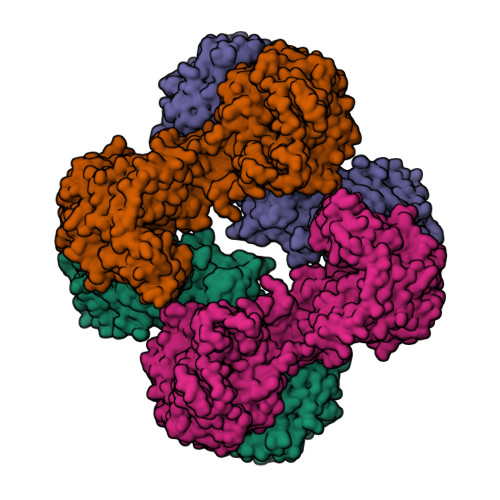
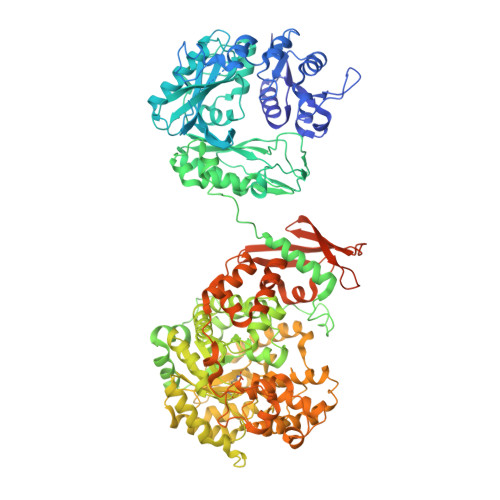
Interaction between the biotin carboxyl carrier domain and the biotin carboxylase domain in pyruvate carboxylase from Rhizobium etli.
Lietzan, A.D., Menefee, A.L., Zeczycki, T.N., Kumar, S., Attwood, P.V., Wallace, J.C., Cleland, W.W., St Maurice, M.(2011) Biochemistry 50: 9708-9723
- PubMed: 21958016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi201277j
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3TW6, 3TW7 - PubMed Abstract:
Pyruvate carboxylase (PC) catalyzes the ATP-dependent carboxylation of pyruvate to oxaloacetate, an important anaplerotic reaction in mammalian tissues. To effect catalysis, the tethered biotin of PC must gain access to active sites in both the biotin carboxylase domain and the carboxyl transferase domain. Previous studies have demonstrated that a mutation of threonine 882 to alanine in PC from Rhizobium etli renders the carboxyl transferase domain inactive and favors the positioning of biotin in the biotin carboxylase domain. We report the 2.4 Å resolution X-ray crystal structure of the Rhizobium etli PC T882A mutant which reveals the first high-resolution description of the domain interaction between the biotin carboxyl carrier protein domain and the biotin carboxylase domain. The overall quaternary arrangement of Rhizobium etli PC remains highly asymmetrical and is independent of the presence of allosteric activator. While biotin is observed in the biotin carboxylase domain, its access to the active site is precluded by the interaction between Arg353 and Glu248, revealing a mechanism for regulating carboxybiotin access to the BC domain active site. The binding location for the biotin carboxyl carrier protein domain demonstrates that tethered biotin cannot bind in the biotin carboxylase domain active site in the same orientation as free biotin, helping to explain the difference in catalysis observed between tethered biotin and free biotin substrates in biotin carboxylase enzymes. Electron density located in the biotin carboxylase domain active site is assigned to phosphonoacetate, offering a probable location for the putative carboxyphosphate intermediate formed during biotin carboxylation. The insights gained from the T882A Rhizobium etli PC crystal structure provide a new series of catalytic snapshots in PC and offer a revised perspective on catalysis in the biotin-dependent enzyme family.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, Marquette University, Milwaukee, Wisconsin 53201, United States.