Crystallographic portrayal of different conformational states of a Lys49 phospholipase A2 homologue: insights into structural determinants for myotoxicity and dimeric configuration.
Ullah, A., Souza, T.A., Betzel, C., Murakami, M.T., Arni, R.K.(2012) Int J Biol Macromol 51: 209-214
- PubMed: 22584077
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2012.05.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4DCF - PubMed Abstract:
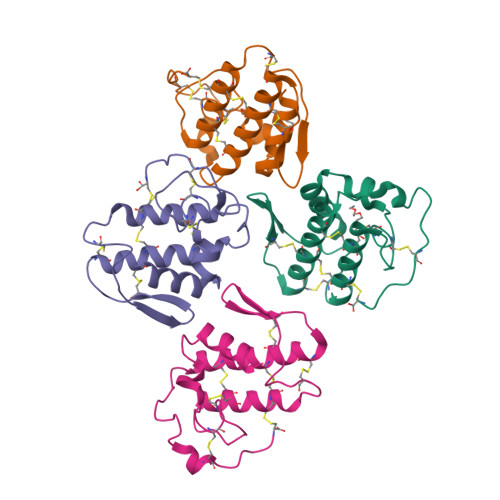
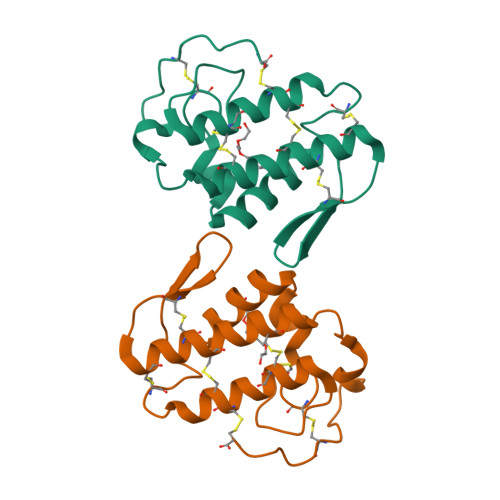
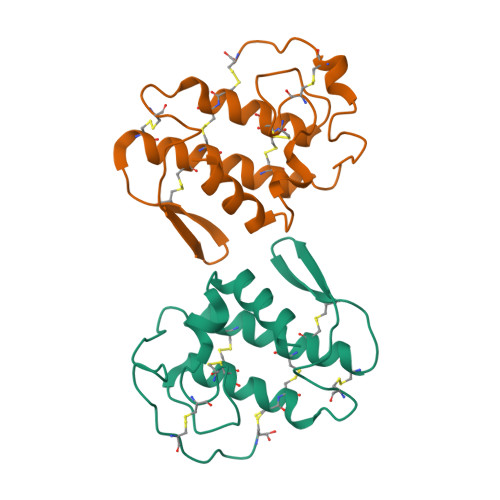
Catalytically inactive phospholipase A(2) (PLA(2)) homologues play key roles in the pathogenesis induced by snake envenomation, causing extensive tissue damage via a mechanism still unknown. Although, the amino acid residues directly involved in catalysis are conserved, the substitution of Asp49 by Arg/Lys/Gln or Ser prevents the binding of the essential calcium ion and hence these proteins are incapable of hydrolyzing phospholipids. In this work, the crystal structure of a Lys49-PLA(2) homologue from Bothrops brazili (MTX-II) was solved in two conformational states: (a) native, with Lys49 singly coordinated by the backbone oxygen atom of Val31 and (b) complexed with tetraethylene glycol (TTEG). Interestingly, the TTEG molecule was observed in two different coordination cages depending on the orientation of the nominal calcium-binding loop and of the residue Lys49. These structural observations indicate a direct role for the residue Lys49 in the functioning of a catalytically inactive PLA(2) homologue suggesting a contribution of the active site-like region in the expression of pharmacological effects such as myotoxicity and edema formation. Despite the several crystal structures of Lys49-PLA(2) homologues already determined, their biological assembly remains controversial with two possible conformations. The extended dimer with the hydrophobic channel exposed to the solvent and the compact dimer in which the active site-like region is occluded by the dimeric interface. In the MTX-II crystal packing analysis was found only the extended dimer as a possible stable quaternary arrangement.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centro Multiusuário de Inovação Biomolecular, Departamento de Física, Universidade Estadual Paulista, São José do Rio Preto-SP, 15054-000 SP, Brazil.