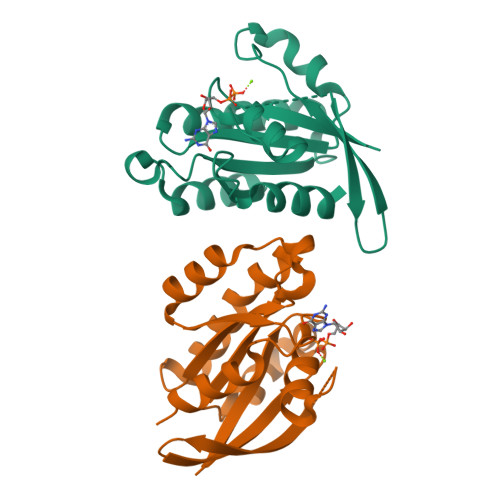
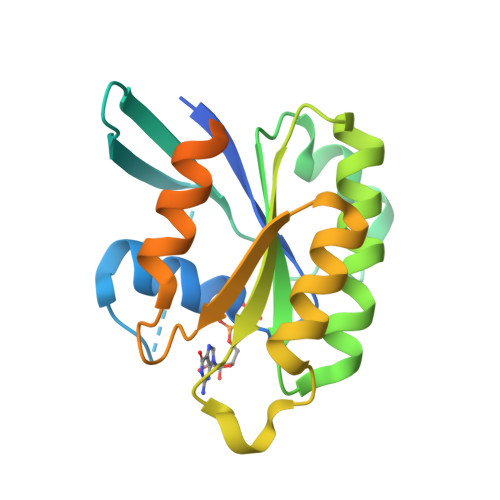
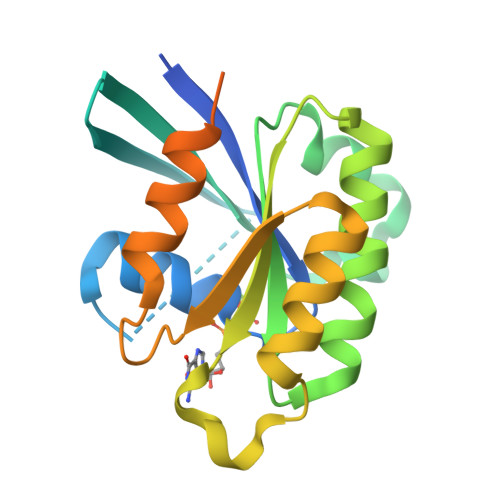
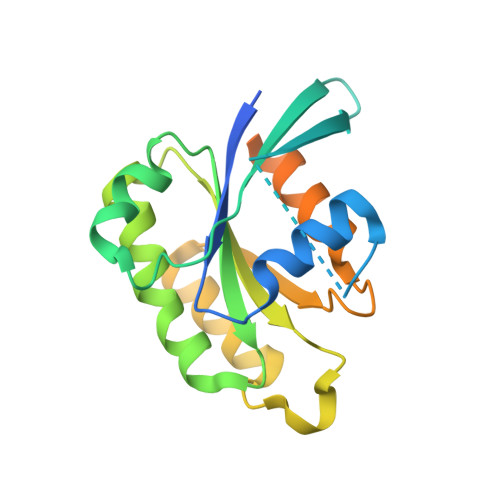
Crystal structure of Rab6A'(Q72L) mutant reveals unexpected GDP/Mg2+ binding with opened GTP-binding domain
Shin, Y.-C., Yoon, J.H., Jang, T.-H., Kim, S.Y., Heo, W.D., So, I., Jeon, J.-H., Park, H.H.(2012) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 424: 269-273
- PubMed: 22750005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.06.102
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4DKX - PubMed Abstract:
The Ras small G protein-superfamily is a family of GTP hydrolases whose activity is regulated by GTP/GDP binding states. Rab6A, a member of the Ras superfamily, is involved in the regulation of vesicle trafficking, which is critical for endocytosis, biosynthesis, secretion, cell differentiation and cell growth. Rab6A exists in two isoforms, termed RabA and Rab6A'. Substitution of Gln72 to Leu72 (Q72L) at Rab6 family blocks GTP hydrolysis activity and this mutation usually causes the Rab6 protein to be constitutively in an active form. Here, we report the crystal structure of the human Rab6A'(Q72L) mutant form at 1.9Å resolution. Unexpectedly, we found that Rab6A'(Q72L) possesses GDP/Mg(2+) in the GTP binding pockets, which is formed by a flexible switch I and switch II. Large conformational changes were also detected in the switch I and switch II regions. Our structure revealed that the non-hydrolysable, constitutively active form of Rab6A' can accommodate GDP/Mg(2+) in the open conformation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Physiology and Biomedical Sciences, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-799, South Korea.