Structure determination and refinement of the Humicola insolens endoglucanase V at 1.5 A resolution.
Davies, G.J., Dodson, G., Moore, M.H., Tolley, S.P., Dauter, Z., Wilson, K.S., Rasmussen, G., Schulein, M.(1996) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 52: 7-17
- PubMed: 15299721
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444995009280
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3ENG, 4ENG - PubMed Abstract:
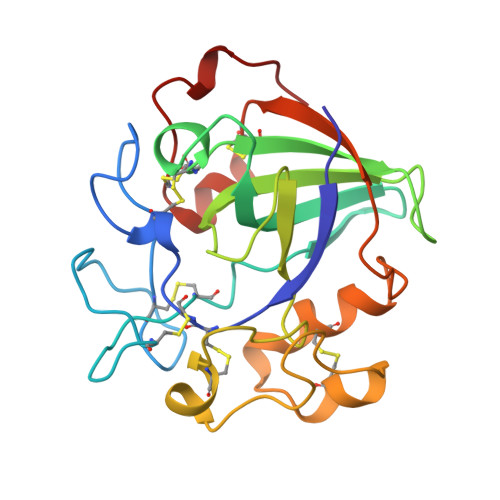
The structure of the catalytic core of the endoglucanase V (EGV) from Humicola insolens has been determined by the method of multiple isomorphous replacement at 1.5 A resolution. The final model, refined with X-PLOR and PROLSQ, has a crystallographic R factor of 0.163 (R(free) = 0.240) with deviations from stereochemical target values of 0.012 A and 0.037 degrees for bonds and angles, respectively. The model was further refined with SHELXL, including anisotropic modelling of the protein-atom temperature factors, to give a final model with an R factor of 0.105 and an R(free) of 0.154. The initial isomorphous replacement electron-density map was poor and uninterpretable but was improved by the use of synchrotron data collected at a wavelength chosen so as to optimize the f" contribution of the anomalous scattering from the heavy atoms. The structure of H. insolens EGV consists of a six-stranded beta-barrel domain, similar to that found in a family of plant defence proteins, linked by a number of disulfide-bonded loop regions. A long open groove runs across the surface of the enzyme either side of which lie the catalytic aspartate residues. The 9 A separation of the catalytic carboxylate groups is consistent with the observation that EGV catalyzes the hydrolysis of the cellulose, beta(1-->4) links with inversion of configuration at the anomeric C1 atom. This structure is the first representative from the glycosyl hydrolase family 45.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of York, Heslington, England.