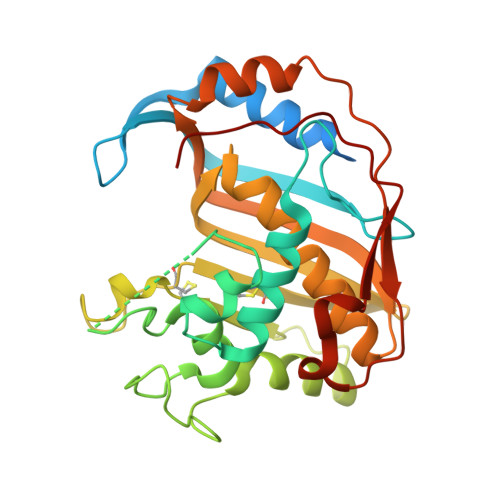
Alanine mutants of the interface residues of human thymidylate synthase decode key features of the binding mode of allosteric anticancer peptides.
Tochowicz, A., Santucci, M., Saxena, P., Guaitoli, G., Trande, M., Finer-Moore, J., Stroud, R.M., Costi, M.P.(2015) J Med Chem 58: 1012-1018
- PubMed: 25427005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm5011176
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4FGT - PubMed Abstract:
Allosteric peptide inhibitors of thymidylate synthase (hTS) bind to the dimer interface and stabilize the inactive form of the protein. Four interface residues were mutated to alanine, and interaction studies were employed to decode the key role of these residues in the peptide molecular recognition. This led to the identification of three crucial interface residues F59, L198, and Y202 that impart activity to the peptide inhibitors and suggest the binding area for further inhibitor design.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, University of California-San Francisco , 600 16th Street, San Francisco, California 94158, United States.