Structure and function of phosphonoacetaldehyde dehydrogenase: the missing link in phosphonoacetate formation.
Agarwal, V., Peck, S.C., Chen, J.H., Borisova, S.A., Chekan, J.R., van der Donk, W.A., Nair, S.K.(2014) Chem Biol 21: 125-135
- PubMed: 24361046
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2013.11.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4I3T, 4I3U, 4I3V, 4I3W, 4I3X - PubMed Abstract:
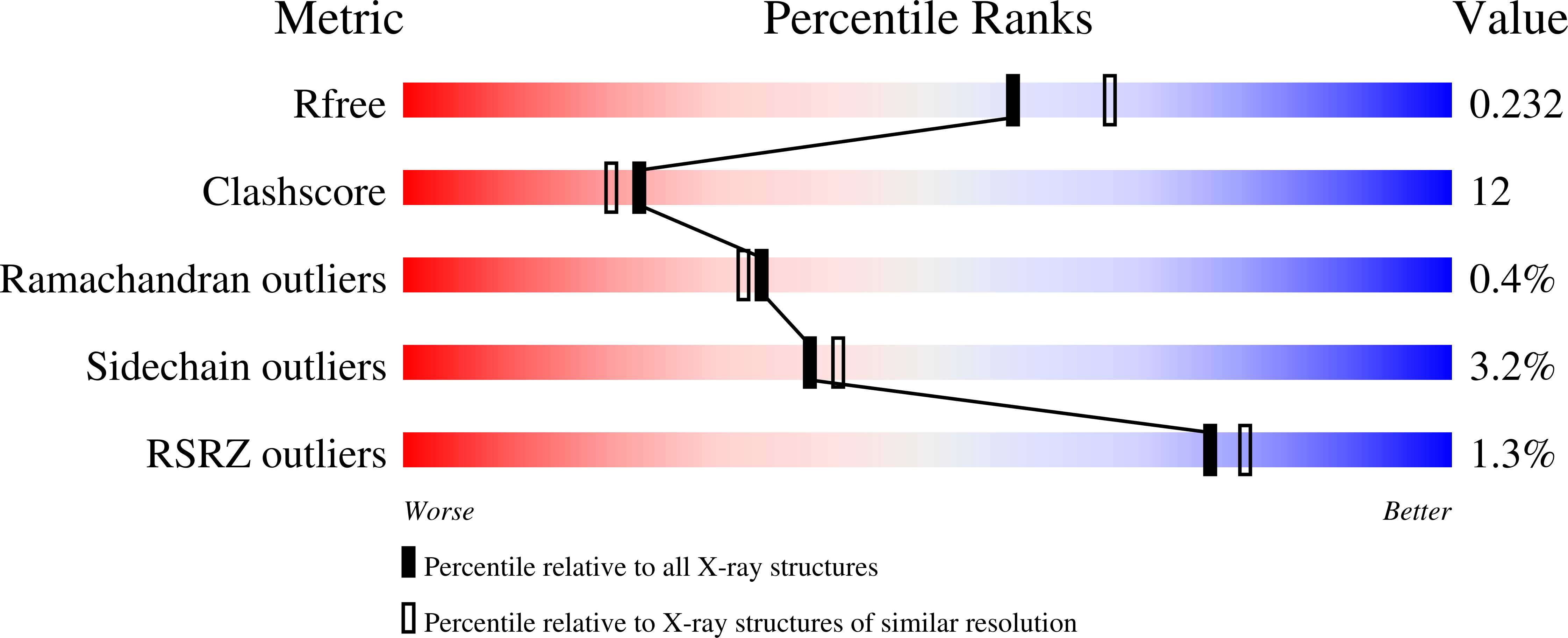
Phosphonates (C-PO₃²⁻) have applications as antibiotics, herbicides, and detergents. In some environments, these molecules represent the predominant source of phosphorus, and several microbes have evolved dedicated enzymatic machineries for phosphonate degradation. For example, most common naturally occurring phosphonates can be catabolized to either phosphonoacetaldehyde or phosphonoacetate, which can then be hydrolyzed to generate inorganic phosphate and acetaldehyde or acetate, respectively. The phosphonoacetaldehyde oxidase gene (phnY) links these two hydrolytic processes and provides a previously unknown catabolic mechanism for phosphonoacetate production in the microbial metabolome. Here, we present biochemical characterization of PhnY and high-resolution crystal structures of the apo state, as well as complexes with substrate, cofactor, and product. Kinetic analysis of active site mutants demonstrates how a highly conserved aldehyde dehydrogenase active site has been modified in nature to generate activity with a phosphonate substrate.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Biophysics and Computational Biology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL 61801, USA; Institute for Genomic Biology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL 61801, USA.