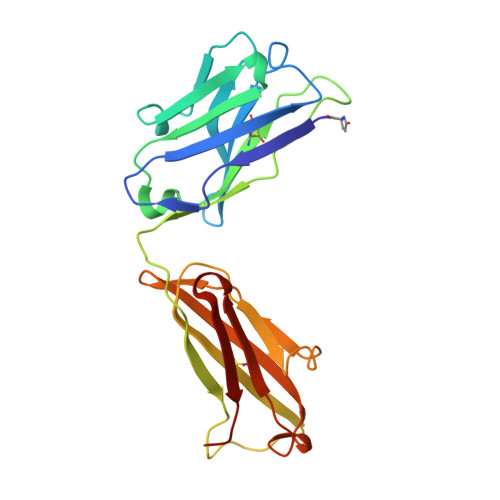
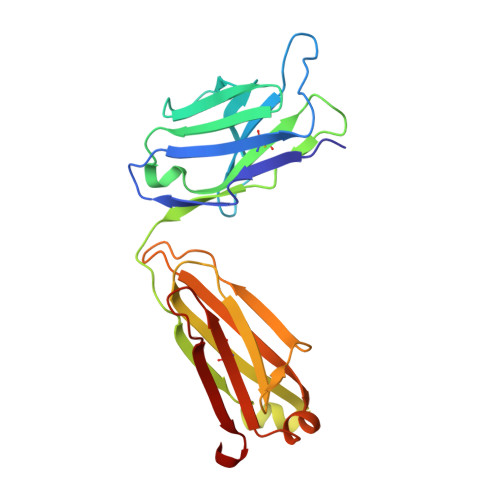
Groove-type Recognition of Chlamydiaceae-specific Lipopolysaccharide Antigen by a Family of Antibodies Possessing an Unusual Variable Heavy Chain N-Linked Glycan.
Haji-Ghassemi, O., Muller-Loennies, S., Saldova, R., Muniyappa, M., Brade, L., Rudd, P.M., Harvey, D.J., Kosma, P., Brade, H., Evans, S.V.(2014) J Biol Chem 289: 16644-16661
- PubMed: 24682362
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.528224
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4M7J, 4M7Z, 4M93, 4MA1 - PubMed Abstract:
The structure of the antigen binding fragment of mAb S25-26, determined to 1.95 Å resolution in complex with the Chlamydiaceae family-specific trisaccharide antigen Kdo(2→8)Kdo(2→4)Kdo (Kdo = 3-deoxy-α-d-manno-oct-2-ulopyranosonic acid), displays a germ-line-coded paratope that differs significantly from previously characterized Chlamydiaceae-specific mAbs despite being raised against the identical immunogen. Unlike the terminal Kdo recognition pocket that promotes cross-reactivity in S25-2-type antibodies, S25-26 and the closely related S25-23 utilize a groove composed of germ-line residues to recognize the entire trisaccharide antigen and so confer strict specificity. Interest in S25-23 was sparked by its rare high μm affinity and strict specificity for the family-specific trisaccharide antigen; however, only the related antibody S25-26 proved amenable to crystallization. The structures of three unliganded forms of S25-26 have a labile complementary-determining region H3 adjacent to significant glycosylation of the variable heavy chain on asparagine 85 in Framework Region 3. Analysis of the glycan reveals a heterogeneous mixture with a common root structure that contains an unusually high number of terminal αGal-Gal moieties. One of the few reported structures of glycosylated mAbs containing these epitopes is the therapeutic antibody Cetuximab; however, unlike Cetuximab, one of the unliganded structures in S25-26 shows significant order in the glycan with appropriate electron density for nine residues. The elucidation of the three-dimensional structure of an αGal-containing N-linked glycan on a mAb variable heavy chain has potential clinical interest, as it has been implicated in allergic response in patients receiving therapeutic antibodies.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Department of Biochemistry and Microbiology, University of Victoria, Victoria, British Columbia V8P 3P6, Canada.