An ATP Binding Cassette Transporter Mediates the Uptake of alpha-(1,6)-Linked Dietary Oligosaccharides in Bifidobacterium and Correlates with Competitive Growth on These Substrates.
Ejby, M., Fredslund, F., Andersen, J.M., Vujicic Zagar, A., Henriksen, J.R., Andersen, T.L., Svensson, B., Slotboom, D.J., Abou Hachem, M.(2016) J Biological Chem 291: 20220-20231
- PubMed: 27502277
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.746529
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4ZS9, 4ZZA, 4ZZE - PubMed Abstract:
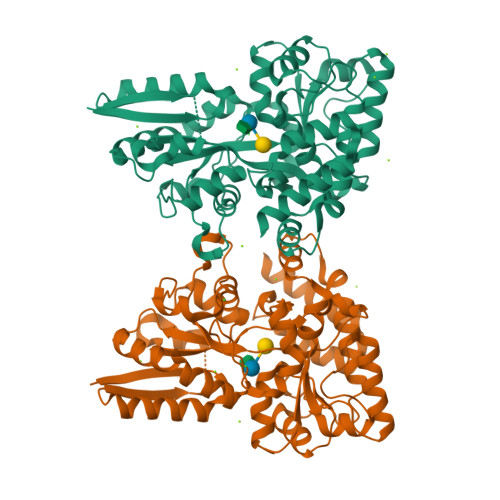
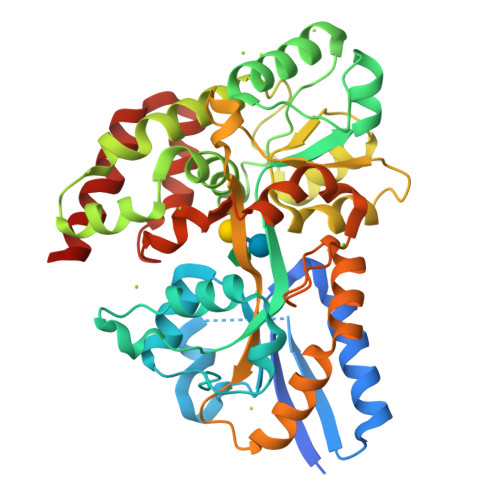
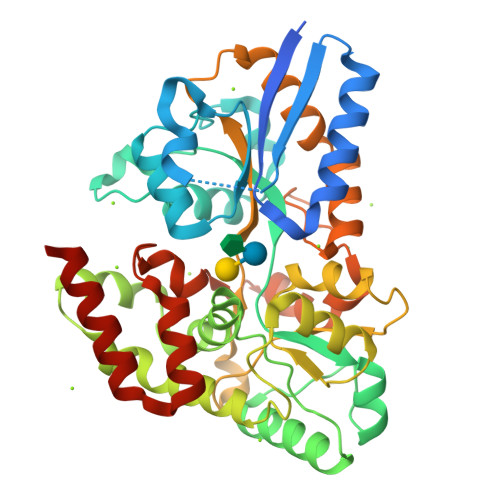
The molecular details and impact of oligosaccharide uptake by distinct human gut microbiota (HGM) are currently not well understood. Non-digestible dietary galacto- and gluco-α-(1,6)-oligosaccharides from legumes and starch, respectively, are preferentially fermented by mainly bifidobacteria and lactobacilli in the human gut. Here we show that the solute binding protein (BlG16BP) associated with an ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter from the probiotic Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis Bl-04 binds α-(1,6)-linked glucosides and galactosides of varying size, linkage, and monosaccharide composition with preference for the trisaccharides raffinose and panose. This preference is also reflected in the α-(1,6)-galactoside uptake profile of the bacterium. Structures of BlG16BP in complex with raffinose and panose revealed the basis for the remarkable ligand binding plasticity of BlG16BP, which recognizes the non-reducing α-(1,6)-diglycoside in its ligands. BlG16BP homologues occur predominantly in bifidobacteria and a few Firmicutes but lack in other HGMs. Among seven bifidobacterial taxa, only those possessing this transporter displayed growth on α-(1,6)-glycosides. Competition assays revealed that the dominant HGM commensal Bacteroides ovatus was out-competed by B. animalis subsp. lactis Bl-04 in mixed cultures growing on raffinose, the preferred ligand for the BlG16BP. By comparison, B. ovatus mono-cultures grew very efficiently on this trisaccharide. These findings suggest that the ABC-mediated uptake of raffinose provides an important competitive advantage, particularly against dominant Bacteroides that lack glycan-specific ABC-transporters. This novel insight highlights the role of glycan transport in defining the metabolic specialization of gut bacteria.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Protein Glycoscience and Biotechnology, Department of Bioengineering, Elektrovej, Building 375.