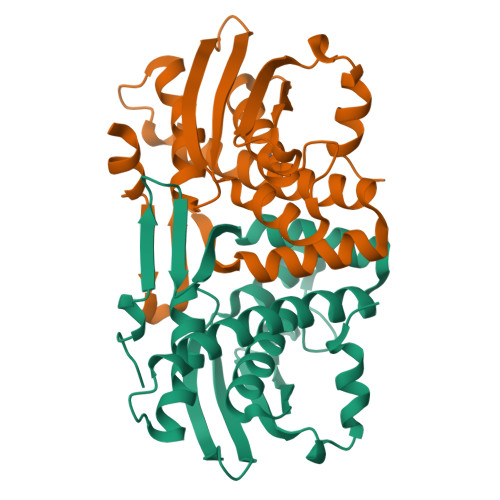
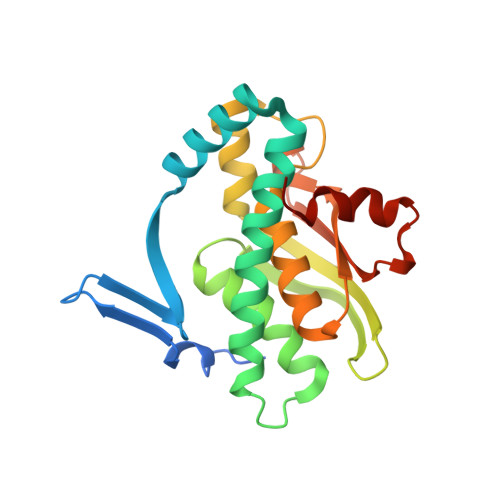
Structural Analysis of the Phenol-Responsive Sensory Domain of the Transcription Activator Poxr
Patil, V.V., Park, K.-H., Lee, S.-G., Woo, E.J.(2016) Structure 624: 24
- PubMed: 27050690
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2016.03.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5FRU, 5FRV, 5FRW, 5FRX, 5FRY, 5FRZ, 5FS0 - PubMed Abstract:
Positive phenol-degradative gene regulator (PoxR) is a σ(54)-dependent AAA+ ATPase transcription activator that regulates the catabolism of phenols. The PoxR sensory domain detects phenols and relays signals for the activation of transcription. Here we report the first structure of the phenol sensory domain bound to phenol and five derivatives. It exists as a tightly intertwined homodimer with a phenol-binding pocket buried inside, placing two C termini on the same side of the dimer. His102 and Trp130 interact with the hydroxyl group of the phenol in a cavity surrounded by rigid hydrophobic residues on one side and a flexible region on the other. Each monomer has a V4R fold with a unique zinc-binding site. A shift at the C-terminal helix suggests that there is a possible conformational change upon ligand binding. The results provide a structural basis of chemical effector binding for transcriptional regulation with broad implications for protein engineering.
Organizational Affiliation:
Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Daejeon 305-806, Korea; Department of Bio-Analytical science, University of Science and Technology, Daejeon 305-333, Korea.