Mechanistic insights into caspase-9 activation by the structure of the apoptosome holoenzyme
Li, Y., Zhou, M., Hu, Q., Bai, X.-C., Huang, W., Scheres, S.H.W., Shi, Y.(2017) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114: 1542-1547
- PubMed: 28143931
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1620626114
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5WVE - PubMed Abstract:
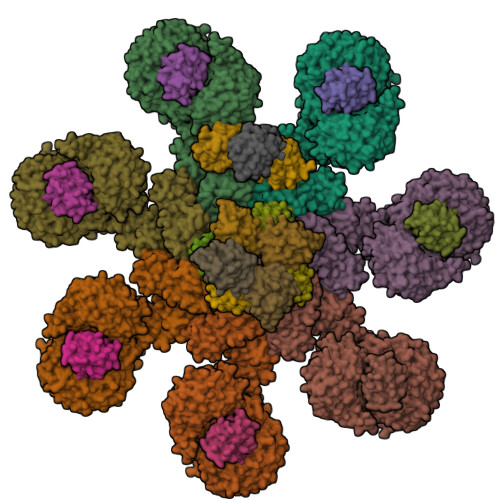
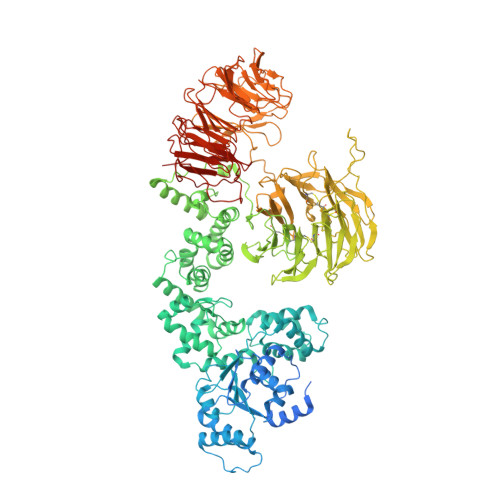
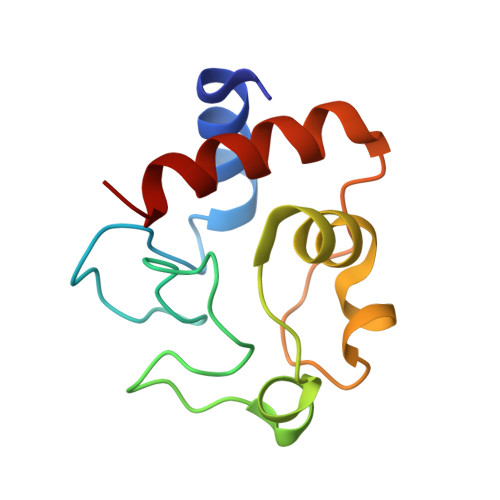
Mammalian intrinsic apoptosis requires activation of the initiator caspase-9, which then cleaves and activates the effector caspases to execute cell killing. The heptameric Apaf-1 apoptosome is indispensable for caspase-9 activation by together forming a holoenzyme. The molecular mechanism of caspase-9 activation remains largely enigmatic. Here, we report the cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of an apoptotic holoenzyme and structure-guided biochemical analyses. The caspase recruitment domains (CARDs) of Apaf-1 and caspase-9 assemble in two different ways: a 4:4 complex docks onto the central hub of the apoptosome, and a 2:1 complex binds the periphery of the central hub. The interface between the CARD complex and the central hub is required for caspase-9 activation within the holoenzyme. Unexpectedly, the CARD of free caspase-9 strongly inhibits its proteolytic activity. These structural and biochemical findings demonstrate that the apoptosome activates caspase-9 at least in part through sequestration of the inhibitory CARD domain.
Organizational Affiliation:
Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology, Tsinghua-Peking Center for Life Sciences, School of Life Sciences and School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China.