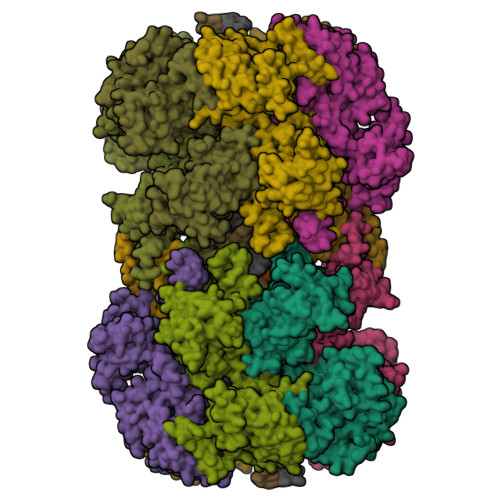
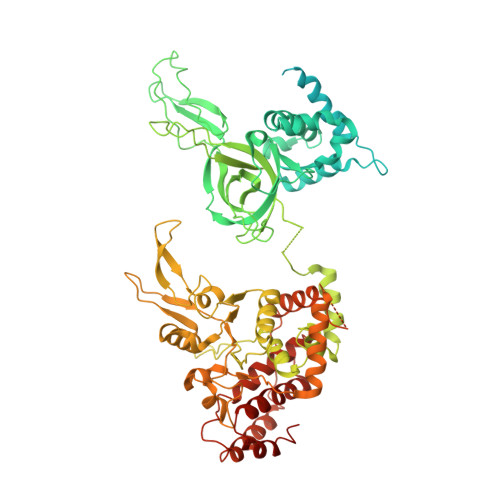
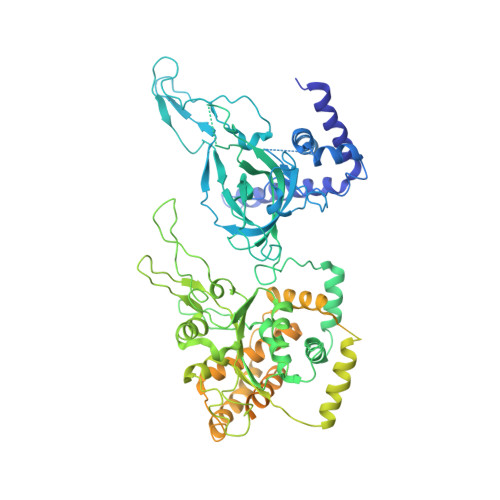
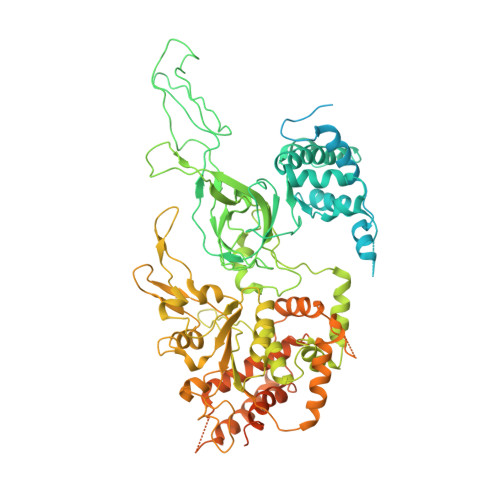
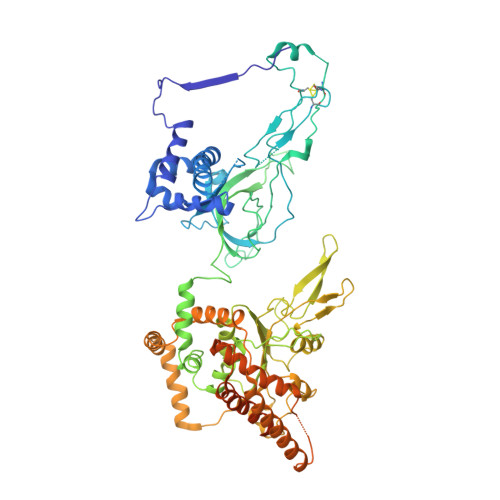
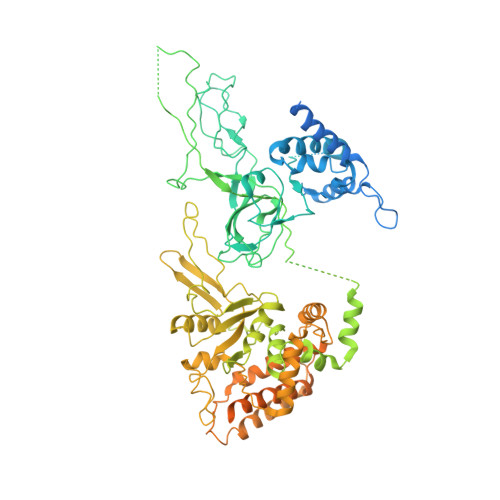
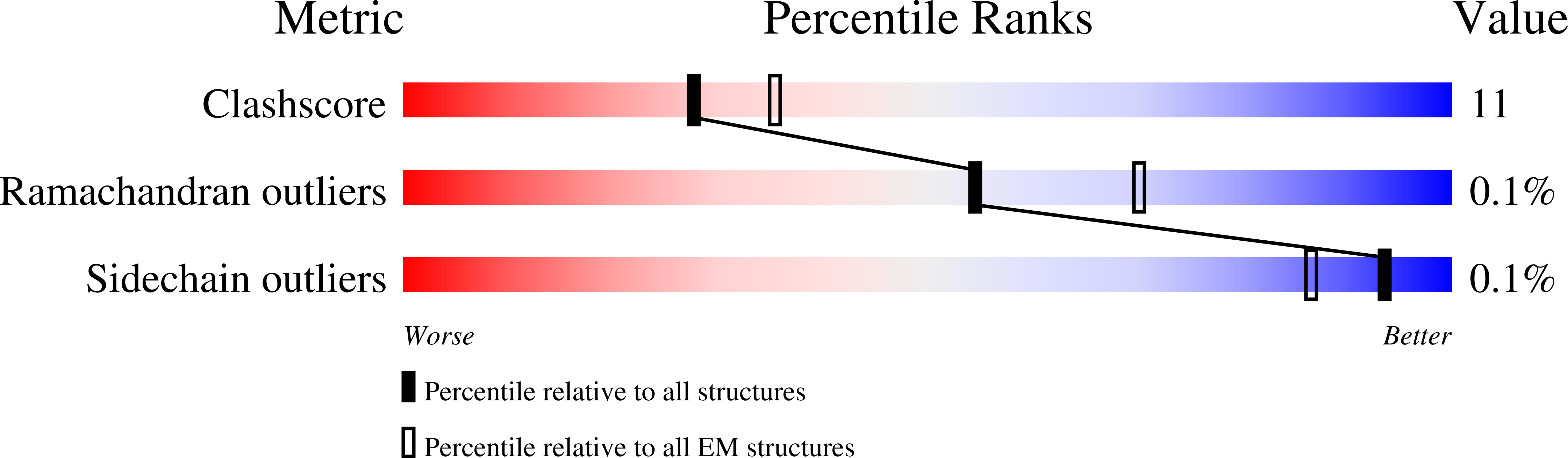Cryo-EM structure of a licensed DNA replication origin.
Abid Ali, F., Douglas, M.E., Locke, J., Pye, V.E., Nans, A., Diffley, J.F.X., Costa, A.(2017) Nat Commun 8: 2241-2241
- PubMed: 29269875
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02389-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6F0L - PubMed Abstract:
Eukaryotic origins of replication are licensed upon loading of the MCM helicase motor onto DNA. ATP hydrolysis by MCM is required for loading and the post-catalytic MCM is an inactive double hexamer that encircles duplex DNA. Origin firing depends on MCM engagement of Cdc45 and GINS to form the CMG holo-helicase. CMG assembly requires several steps including MCM phosphorylation by DDK. To understand origin activation, here we have determined the cryo-EM structures of DNA-bound MCM, either unmodified or phosphorylated, and visualize a phospho-dependent MCM element likely important for Cdc45 recruitment. MCM pore loops touch both the Watson and Crick strands, constraining duplex DNA in a bent configuration. By comparing our new MCM-DNA structure with the structure of CMG-DNA, we suggest how the conformational transition from the loaded, post-catalytic MCM to CMG might promote DNA untwisting and melting at the onset of replication.
Organizational Affiliation:
Macromolecular Machines Laboratory, The Francis Crick Institute, 1 Midland Road, London, NW1 1AT, UK.