Potent Antimalarial 2-Pyrazolyl Quinolonebc1(Qi) Inhibitors with Improved Drug-like Properties.
David Hong, W., Leung, S.C., Amporndanai, K., Davies, J., Priestley, R.S., Nixon, G.L., Berry, N.G., Samar Hasnain, S., Antonyuk, S., Ward, S.A., Biagini, G.A., O'Neill, P.M.(2018) ACS Med Chem Lett 9: 1205-1210
- PubMed: 30613327
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00371
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6HAW - PubMed Abstract:
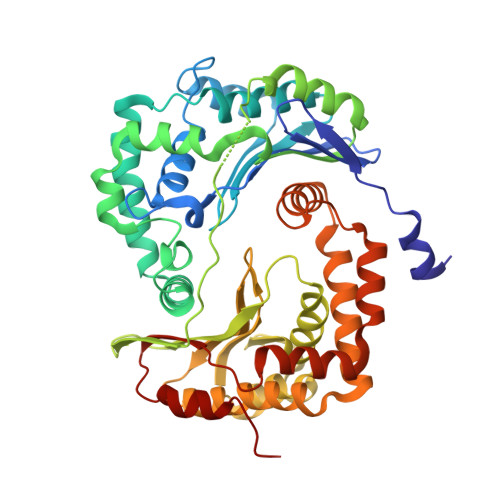
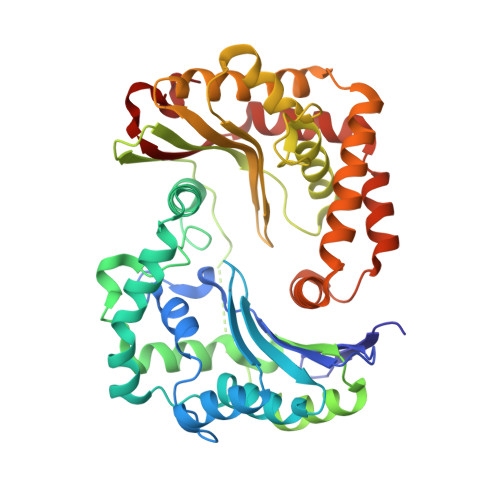
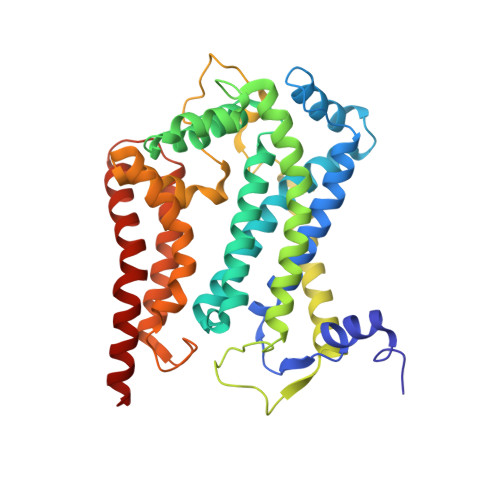
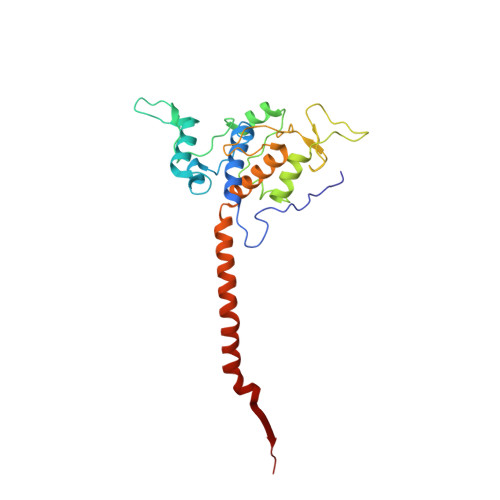
A series of 2-pyrazolyl quinolones has been designed and synthesized in 5-7 steps to optimize for both in vitro antimalarial potency and various in vitro drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics (DMPK) features. The most potent compounds display no cross-resistance with multidrug resistant parasite strains (W2) compared to drug sensitive strains (3D7), with IC 50 (concentration of drug required to achieve half maximal growth suppression) values in the range of 15-33 nM. Furthermore, members of the series retain moderate activity against the atovaquone-resistant parasite isolate (TM90C2B). The described 2-pyrazoyl series displays improved DMPK properties, including improved aqueous solubility compared to previously reported quinolone series and acceptable safety margin through in vitro cytotoxicity assessment. The 2-pyrazolyl quinolones are believed to bind to the ubiquinone-reducing Q i site of the parasite bc 1 complex, which is supported by crystallographic studies of bovine cytochrome bc 1 complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, L69 7ZD, U.K.