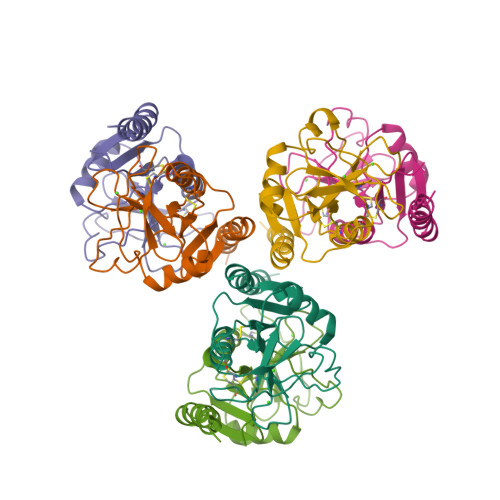
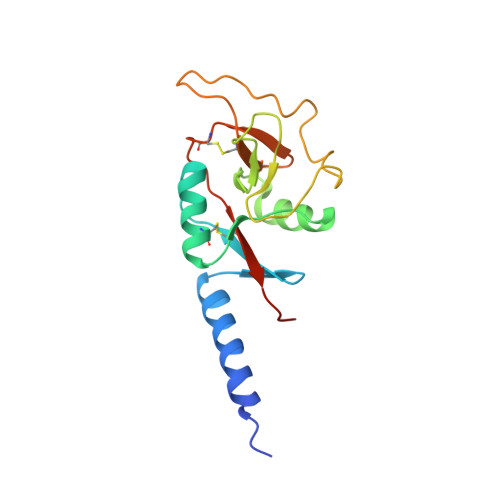
Trimeric structure of the mouse Kupffer cell C-type lectin receptor Clec4f.
Ouyang, Z., Felix, J., Zhou, J., Pei, Y., Ma, B., Hwang, P.M., Lemieux, M.J., Gutsche, I., Zheng, F., Wen, Y.(2020) FEBS Lett 594: 189-198
- PubMed: 31369681
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13565
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6JJJ - PubMed Abstract:
The C-type lectin receptor Clec4f has been identified as a specific surface marker for Kupffer cells, although its ortholog is absent in humans and its biological function remains elusive. Here, we report the crystal structure of a truncated mouse trimeric Clec4f. The orientation between the carbohydrate-recognition domain of Clec4f and its neck region differs from other C-type lectins, resulting in an observed distance of 45 Å between the glycan-binding sites within the Clec4f trimer. Interestingly, the trimeric coiled-coil interface within its heptad neck region contains multiple polyglutamine interactions instead of the predominantly hydrophobic leucine zipper found in other C-type lectin receptors. The Clec4f trimeric structure displays unique features regarding its assembly and ligand recognition, shedding light on the evolution and diversity of the C-type lectin family.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Key Laboratory of Biomedical Information Engineering of Ministry of Education, School of Life Science and Technology, Xi'an Jiaotong University, China.