Discovery of a C-8 hydroxychromene as a potent degrader of estrogen receptor alpha with improved rat oral exposure over GDC-0927.
Labadie, S.S., Li, J., Blake, R.A., Chang, J.H., Goodacre, S., Hartman, S.J., Liang, W., Kiefer, J.R., Kleinheinz, T., Lai, T., Liao, J., Ortwine, D.F., Mody, V., Ray, N.C., Roussel, F., Vinogradova, M., Yeap, S.K., Zhang, B., Zheng, X., Zbieg, J.R., Liang, J., Wang, X.(2019) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 29: 2090-2093
- PubMed: 31311734
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.07.013
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
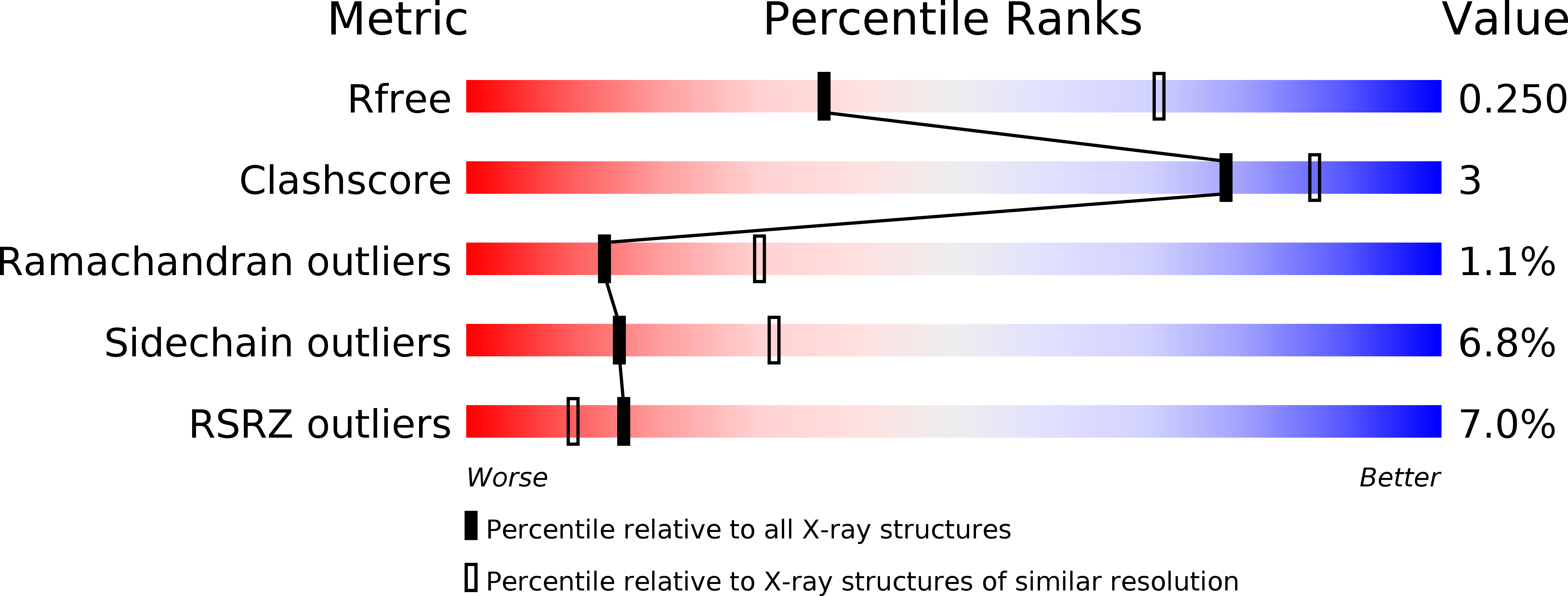
6PET, 6PFM - PubMed Abstract:
Phenolic groups are responsible for the high clearance and low oral bioavailability of the estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) clinical candidate GDC-0927. An exhaustive search for a backup molecule with improved pharmacokinetic (PK) properties identified several metabolically stable analogs, although in general at the expense of the desired potency and degradation efficiency. C-8 hydroxychromene 30 is the first example of a phenol-containing chromene that not only maintained excellent potency but also exhibited 10-fold higher oral exposure in rats. The improved in vivo clearance in rat was hypothesized to be the result of C-8 hydroxy group being sterically protected from glucuronide conjugation. The excellent potency underscores the possibility of replacing the presumed indispensable phenolic group at C-6 or C-7 of the chromene core. Co-crystal structures were obtained to highlight the change in key interactions and rationalize the retained potency.
Organizational Affiliation:
Genentech Inc., South San Francisco, CA 94080, USA.