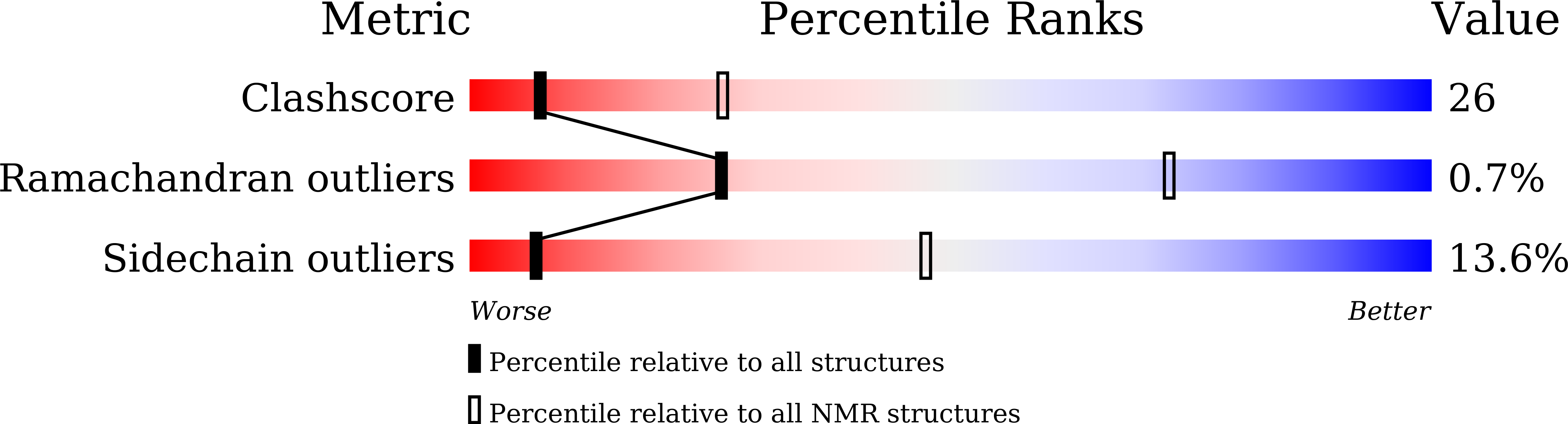Structural and dynamical insights into the PH domain of p62 in human TFIIH.
Okuda, M., Ekimoto, T., Kurita, J.I., Ikeguchi, M., Nishimura, Y.(2021) Nucleic Acids Res 49: 2916-2930
- PubMed: 33211877
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa1045
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7BUL - PubMed Abstract:
TFIIH is a crucial transcription and DNA repair factor consisting of the seven-subunit core. The core subunit p62 contains a pleckstrin homology domain (PH-D), which is essential for locating TFIIH at transcription initiation and DNA damage sites, and two BSD (BTF2-like transcription factors, synapse-associated proteins and DOS2-like proteins) domains. A recent cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of human TFIIH visualized most parts of core, except for the PH-D. Here, by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy we have established the solution structure of human p62 PH-D connected to the BSD1 domain by a highly flexible linker, suggesting the flexibility of PH-D in TFIIH. Based on this dynamic character, the PH-D was modeled in the cryo-EM structure to obtain the whole human TFIIH core structure, which indicates that the PH-D moves around the surface of core with a specific but limited spatial distribution; these dynamic structures were refined by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. Furthermore, we built models, also refined by MD simulations, of TFIIH in complex with five p62-binding partners, including transcription factors TFIIEα, p53 and DP1, and nucleotide excision repair factors XPC and UVSSA. The models explain why the PH-D is crucially targeted by these factors, which use their intrinsically disordered acidic regions for TFIIH recruitment.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Medical Life Science, Yokohama City University, 1-7-29 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi-ku, Yokohama 230-0045, Japan.