Double lock of a potent human therapeutic monoclonal antibody against SARS-CoV-2.
Zhu, L., Deng, Y.Q., Zhang, R.R., Cui, Z., Sun, C.Y., Fan, C.F., Xing, X., Huang, W., Chen, Q., Zhang, N.N., Ye, Q., Cao, T.S., Wang, N., Wang, L., Cao, L., Wang, H., Kong, D., Ma, J., Luo, C., Zhang, Y., Nie, J., Sun, Y., Lv, Z., Shaw, N., Li, Q., Li, X.F., Hu, J., Xie, L., Rao, Z., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Qin, C.F.(2021) Natl Sci Rev 8: nwaa297-nwaa297
- PubMed: 34676096
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwaa297
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7CYP - PubMed Abstract:
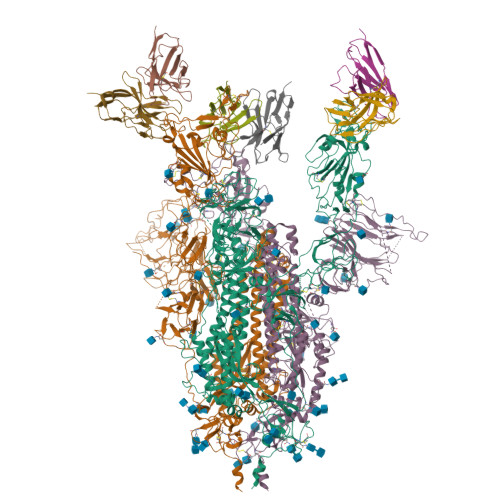
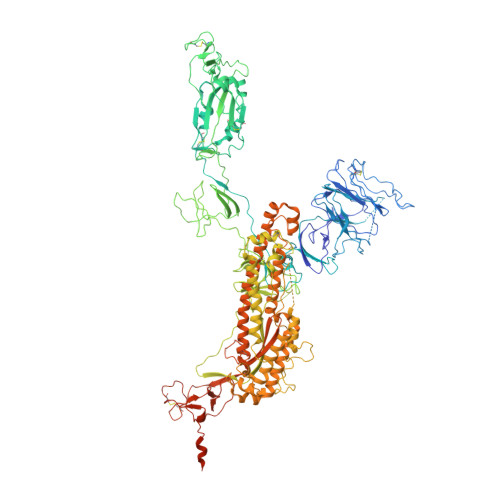
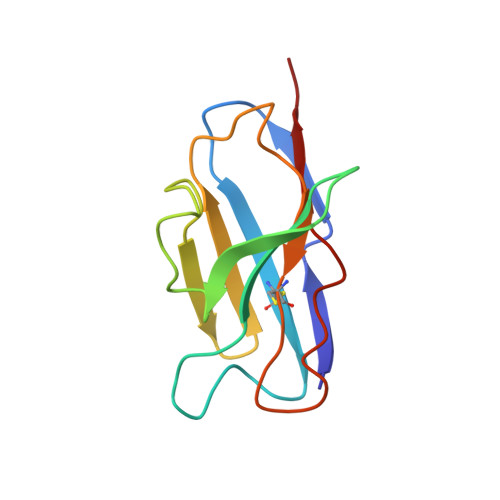
Receptor recognition and subsequent membrane fusion are essential for the establishment of successful infection by SARS-CoV-2. Halting these steps can cure COVID-19. Here we have identified and characterized a potent human monoclonal antibody, HB27, that blocks SARS-CoV-2 attachment to its cellular receptor at sub-nM concentrations. Remarkably, HB27 can also prevent SARS-CoV-2 membrane fusion. Consequently, a single dose of HB27 conferred effective protection against SARS-CoV-2 in two established mouse models. Rhesus macaques showed no obvious adverse events when administrated with 10 times the effective dose of HB27. Cryo-EM studies on complex of SARS-CoV-2 trimeric S with HB27 Fab reveal that three Fab fragments work synergistically to occlude SARS-CoV-2 from binding to the ACE2 receptor. Binding of the antibody also restrains any further conformational changes of the receptor binding domain, possibly interfering with progression from the prefusion to the postfusion stage. These results suggest that HB27 is a promising candidate for immuno-therapies against COVID-19.
Organizational Affiliation:
CAS Key Laboratory of Infection and Immunity, National Laboratory of Macromolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China.