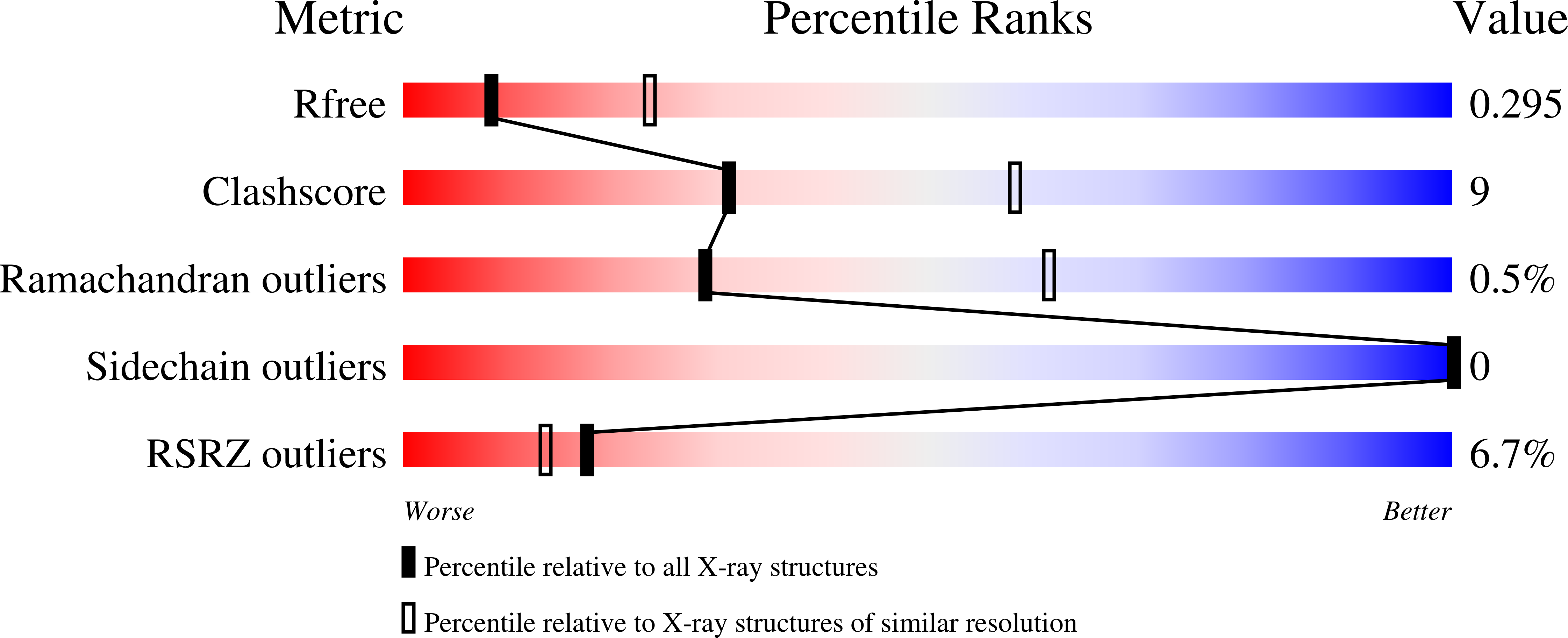
Glioblastoma mutations alter EGFR dimer structure to prevent ligand bias.
Hu, C., Leche 2nd, C.A., Kiyatkin, A., Yu, Z., Stayrook, S.E., Ferguson, K.M., Lemmon, M.A.(2022) Nature 602: 518-522
- PubMed: 35140400
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04393-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7LEN, 7LFR, 7LFS - PubMed Abstract:
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is frequently mutated in human cancer 1,2 , and is an important therapeutic target. EGFR inhibitors have been successful in lung cancer, where mutations in the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain activate the receptor 1 , but not in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) 3 , where mutations occur exclusively in the extracellular region. Here we show that common extracellular GBM mutations prevent EGFR from discriminating between its activating ligands 4 . Different growth factor ligands stabilize distinct EGFR dimer structures 5 that signal with different kinetics to specify or bias outcome 5,6 . EGF itself induces strong symmetric dimers that signal transiently to promote proliferation. Epiregulin (EREG) induces much weaker asymmetric dimers that drive sustained signalling and differentiation 5 . GBM mutations reduce the ability of EGFR to distinguish EREG from EGF in cellular assays, and allow EGFR to form strong (EGF-like) dimers in response to EREG and other low-affinity ligands. Using X-ray crystallography, we further show that the R84K GBM mutation symmetrizes EREG-driven extracellular dimers so that they resemble dimers normally seen with EGF. By contrast, a second GBM mutation, A265V, remodels key dimerization contacts to strengthen asymmetric EREG-driven dimers. Our results argue for an important role of altered ligand discrimination by EGFR in GBM, with potential implications for therapeutic targeting.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmacology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA.