Optimization of Triarylpyridinone Inhibitors of the Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2 to Low-Nanomolar Antiviral Potency.
Zhang, C.H., Spasov, K.A., Reilly, R.A., Hollander, K., Stone, E.A., Ippolito, J.A., Liosi, M.E., Deshmukh, M.G., Tirado-Rives, J., Zhang, S., Liang, Z., Miller, S.J., Isaacs, F., Lindenbach, B.D., Anderson, K.S., Jorgensen, W.L.(2021) ACS Med Chem Lett 12: 1325-1332
- PubMed: 34408808
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.1c00326
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
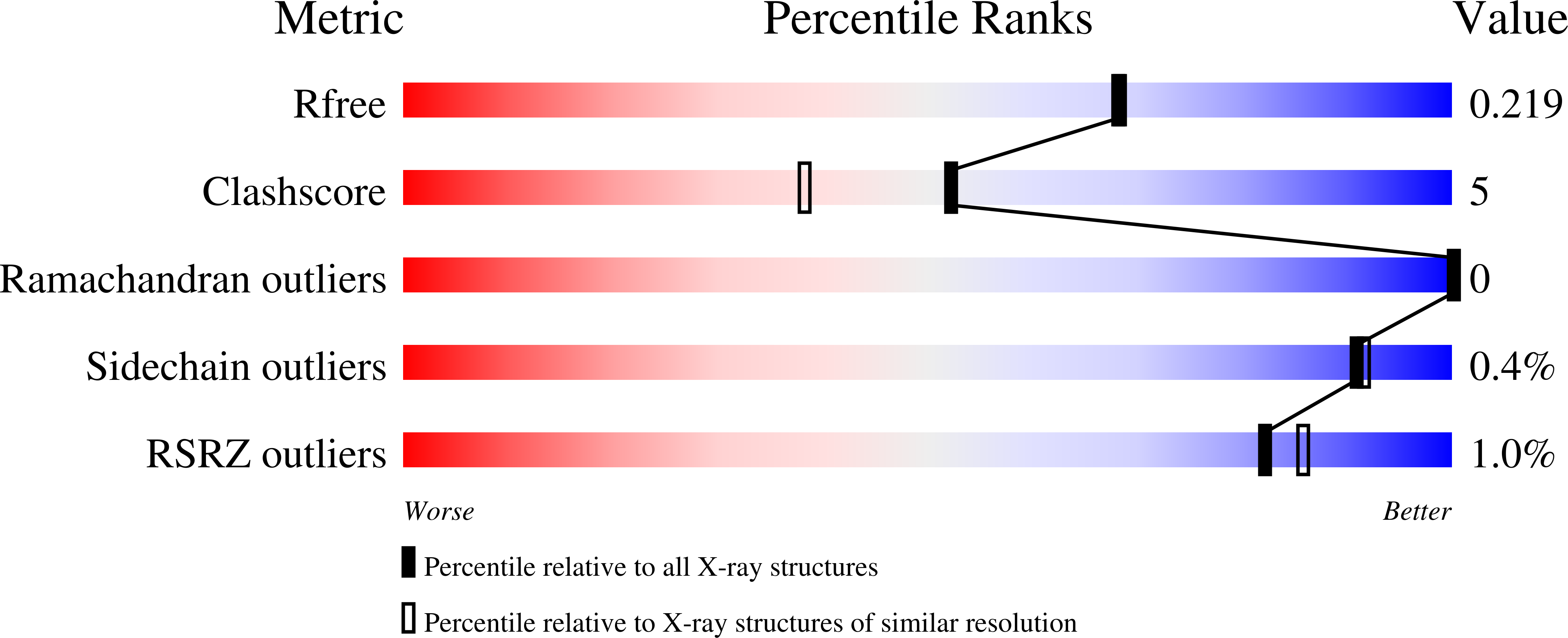
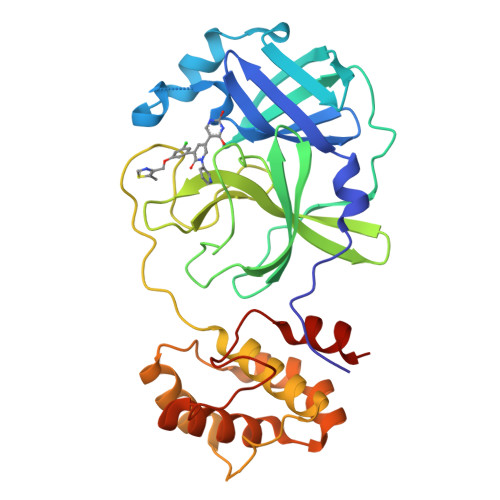
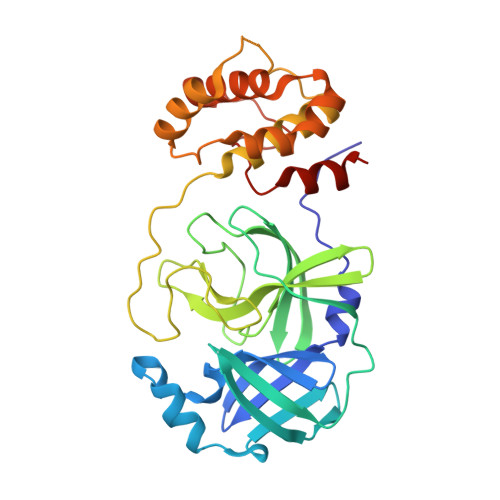
7N44 - PubMed Abstract:
Non-covalent inhibitors of the main protease (M pro ) of SARS-CoV-2 having a pyridinone core were previously reported with IC 50 values as low as 0.018 μM for inhibition of enzymatic activity and EC 50 values as low as 0.8 μM for inhibition of viral replication in Vero E6 cells. The series has now been further advanced by consideration of placement of substituted five-membered-ring heterocycles in the S4 pocket of M pro and N-methylation of a uracil ring. Free energy perturbation calculations provided guidance on the choice of the heterocycles, and protein crystallography confirmed the desired S4 placement. Here we report inhibitors with EC 50 values as low as 0.080 μM, while remdesivir yields values of 0.5-2 μM in side-by-side testing with infectious SARS-CoV-2. A key factor in the improvement is enhanced cell permeability, as reflected in PAMPA measurements. Compounds 19 and 21 are particularly promising as potential therapies for COVID-19, featuring IC 50 values of 0.044-0.061 μM, EC 50 values of ca. 0.1 μM, good aqueous solubility, and no cytotoxicity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06520-8107, United States.