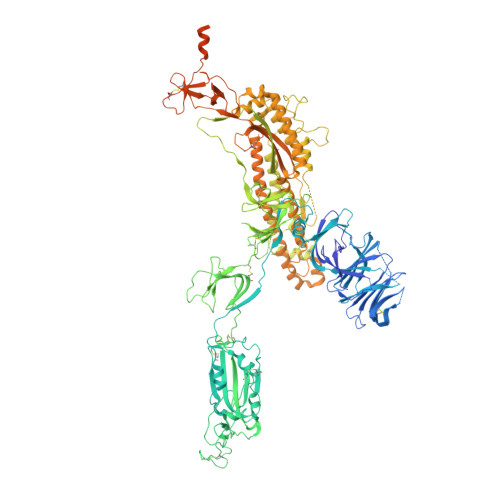
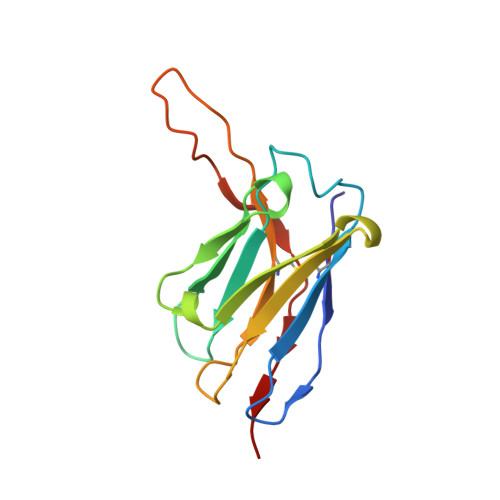
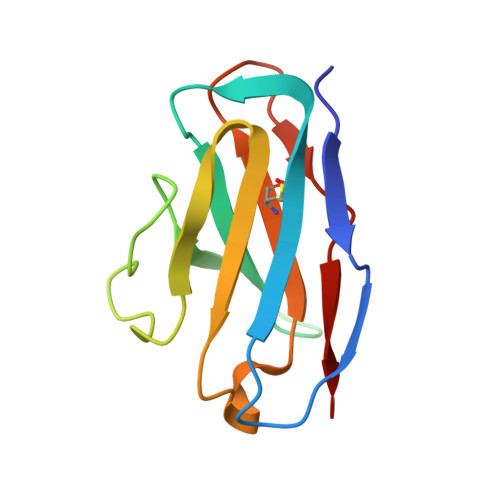
A monoclonal antibody that neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 variants, SARS-CoV, and other sarbecoviruses.
Wang, P., Casner, R.G., Nair, M.S., Yu, J., Guo, Y., Wang, M., Chan, J.F., Cerutti, G., Iketani, S., Liu, L., Sheng, Z., Chen, Z., Yuen, K.Y., Kwong, P.D., Huang, Y., Shapiro, L., Ho, D.D.(2022) Emerg Microbes Infect 11: 147-157
- PubMed: 34836485
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/22221751.2021.2011623
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7N5H - PubMed Abstract:
The repeated emergence of highly pathogenic human coronaviruses as well as their evolving variants highlight the need to develop potent and broad-spectrum antiviral therapeutics and vaccines. By screening monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) isolated from COVID-19-convalescent patients, we found one mAb, 2-36, with cross-neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV. We solved the cryo-EM structure of 2-36 in complex with SARS-CoV-2 or SARS-CoV spike, revealing a highly conserved epitope in the receptor-binding domain (RBD). Antibody 2-36 neutralized not only all current circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants and SARS-COV, but also a panel of bat and pangolin sarbecoviruses that can use human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a receptor. We selected 2-36-escape viruses in vitro and confirmed that K378 T in SARS-CoV-2 RBD led to viral resistance. Taken together, 2-36 represents a strategic reserve drug candidate for the prevention and treatment of possible diseases caused by pre-emergent SARS-related coronaviruses. Its epitope defines a promising target for the development of a pan-sarbecovirus vaccine.
Organizational Affiliation:
Aaron Diamond AIDS Research Center, Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York, NY, USA.