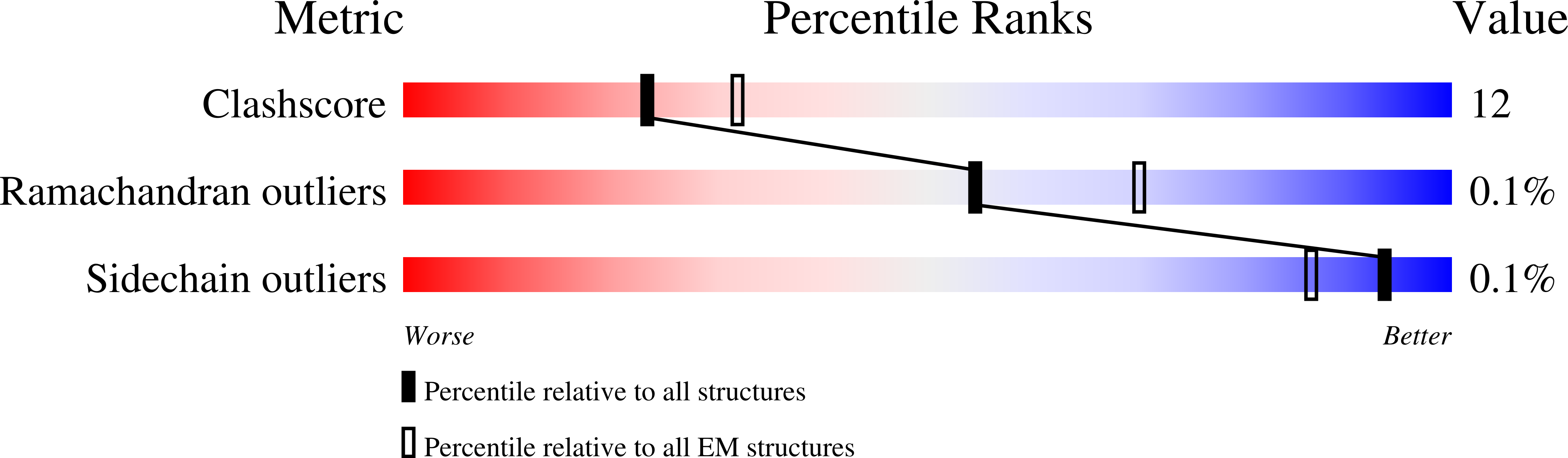A bispecific monomeric nanobody induces spike trimer dimers and neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 in vivo.
Hanke, L., Das, H., Sheward, D.J., Perez Vidakovics, L., Urgard, E., Moliner-Morro, A., Kim, C., Karl, V., Pankow, A., Smith, N.L., Porebski, B., Fernandez-Capetillo, O., Sezgin, E., Pedersen, G.K., Coquet, J.M., Hallberg, B.M., Murrell, B., McInerney, G.M.(2022) Nat Commun 13: 155-155
- PubMed: 35013189
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27610-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7NLL, 7NS6 - PubMed Abstract:
Antibodies binding to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike have therapeutic promise, but emerging variants show the potential for virus escape. This emphasizes the need for therapeutic molecules with distinct and novel neutralization mechanisms. Here we describe the isolation of a nanobody that interacts simultaneously with two RBDs from different spike trimers of SARS-CoV-2, rapidly inducing the formation of spike trimer-dimers leading to the loss of their ability to attach to the host cell receptor, ACE2. We show that this nanobody potently neutralizes SARS-CoV-2, including the beta and delta variants, and cross-neutralizes SARS-CoV. Furthermore, we demonstrate the therapeutic potential of the nanobody against SARS-CoV-2 and the beta variant in a human ACE2 transgenic mouse model. This naturally elicited bispecific monomeric nanobody establishes an uncommon strategy for potent inactivation of viral antigens and represents a promising antiviral against emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Microbiology, Tumor and Cell Biology, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.