Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of C-7 and C-8 Luteolin Derivatives as Influenza Endonuclease Inhibitors.
Reiberger, R., Radilova, K., Kral, M., Zima, V., Majer, P., Brynda, J., Dracinsky, M., Konvalinka, J., Kozisek, M., Machara, A.(2021) Int J Mol Sci 22
- PubMed: 34299354
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147735
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7NUG, 7NUH - PubMed Abstract:
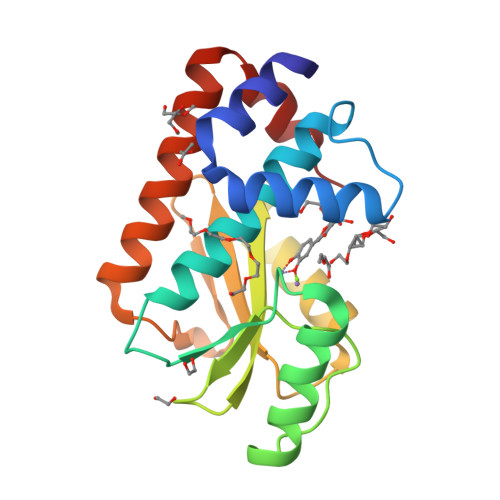
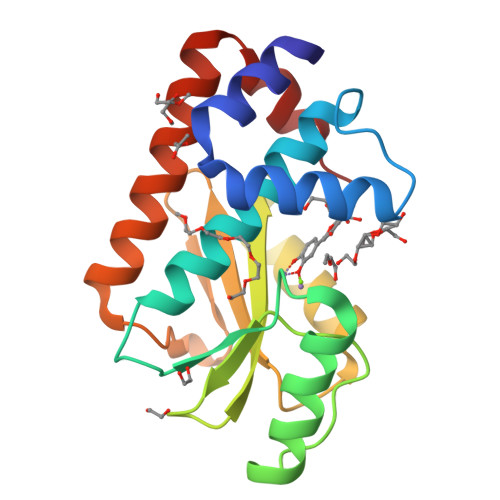
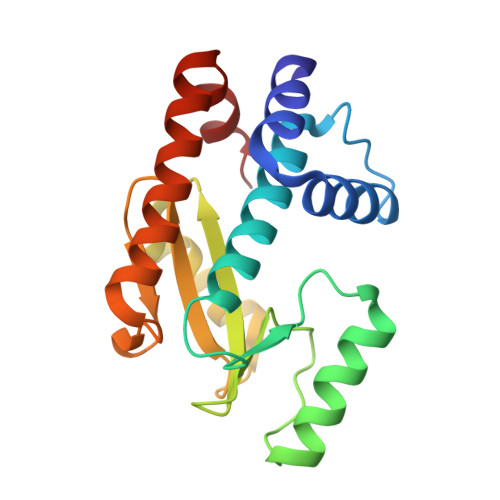
The part of the influenza polymerase PA subunit featuring endonuclease activity is a target for anti-influenza therapies, including the FDA-approved drug Xofluza. A general feature of endonuclease inhibitors is their ability to chelate Mg 2+ or Mn 2+ ions located in the enzyme's catalytic site. Previously, we screened a panel of flavonoids for PA inhibition and found luteolin and its C-glucoside orientin to be potent inhibitors. Through structural analysis, we identified the presence of a 3',4'-dihydroxyphenyl moiety as a crucial feature for sub-micromolar inhibitory activity. Here, we report results from a subsequent investigation exploring structural changes at the C-7 and C-8 positions of luteolin. Experimental IC 50 values were determined by AlphaScreen technology. The most potent inhibitors were C-8 derivatives with inhibitory potencies comparable to that of luteolin. Bio-isosteric replacement of the C-7 hydroxyl moiety of luteolin led to a series of compounds with one-order-of-magnitude-lower inhibitory potencies. Using X-ray crystallography, we solved structures of the wild-type PA-N-terminal domain and its I38T mutant in complex with orientin at 1.9 Å and 2.2 Å resolution, respectively.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Gilead Sciences and IOCB Research Center, Flemingovo n. 2, 166 10 Prague, Czech Republic.